Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
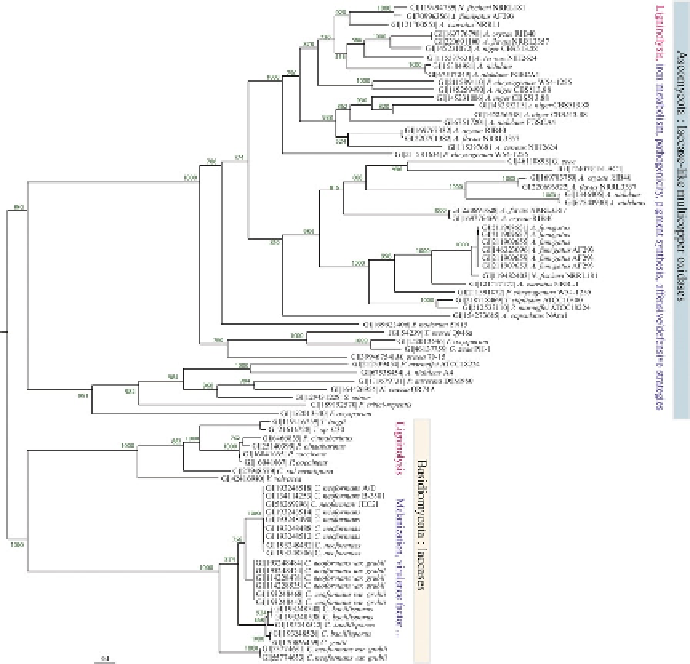
non-redundant databases and integrated into phylogenetic analysis using
maximum likelihood for phylogenetic reconstruction (
Levasseur et al.,
2010
). The strategy involves separate different subfamilies and refines the
laccase family. Phylogenetic analysis enables us to discern two distinct
groups containing the laccases of Basidiomycota and Ascomycota (
Fig. 8
).
Interestingly, Basidiomycota and Ascomycota groups belong to two differ-
ent evolutionary histories, leading to high sequence divergence between
homologs, as evidenced by the tree topology. Functional annotations can
be refined, for example, the Basidiomycota group is divided into two sub-
groups (with 100% bootstrap values) and include not only the laccases
involved in ligninolysis but also the laccases from the pathogenic yeast
Fig. 8. Phylogenetic reconstruction of classical laccases and related laccase-like
multi-copper oxidases. Bootstrapping was carried out with 1000 replications.