Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
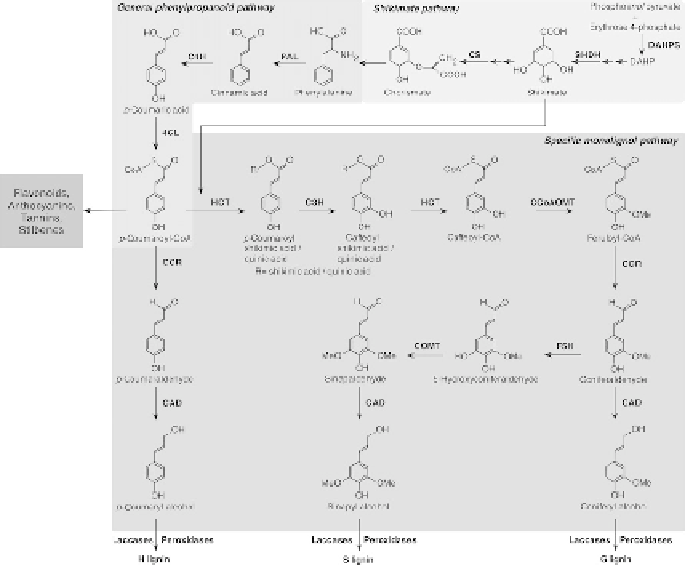
Fig. 1. Phenylpropanoid pathway leading to lignin biosynthesis. The most
favoured route in angiosperms is shown. Enzymes involved in the phenylpropanoid
and monolignol pathways are phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), cinnamate-4-
hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL), p-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:qui-
nate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (HCT), 4-coumarate 3-hydroxylase
(C3H), caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT), cinnamoyl-CoA reductase
(CCR), ferulate (coniferaldehyde)-5-hydroxylase (F5H), caffeic acid/5-hydroxyconi-
feraldehyde O-methyltransferase (COMT), cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD).
The shikimate pathway which provides substrates to the phenylpropanoid pathway is
also shown: 3-deoxyarabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (DAHPS), shiki-
mate dehydrogenase (SHDH), chorismate synthase (CS).
the phenylpropanoid pathway, the deamination of phenylalanine to cin-
namic acid. In the subsequent two steps, cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H)
and 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL) give rise to p-coumaroyl-CoA, one of
the most important branch points of the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis
pathway. From this point, the p-coumaryl alcohol (precursor of H lignin) is
synthesized in two steps requiring cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR) and
cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD). The production of coniferyl alco-
hol (precursor of G lignin) and sinapyl alcohol (precursor of S lignin) needs
supplementary steps. A decisive step for both monolignols is initiated by