Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
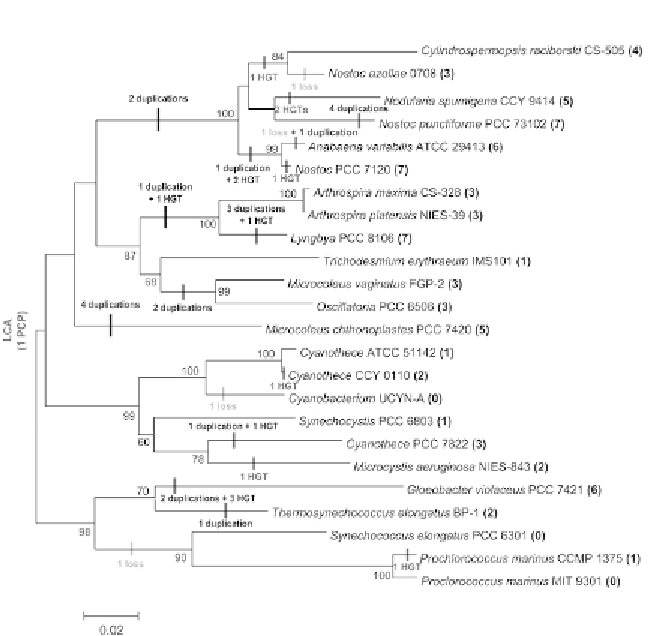
Figure 7.6
Proposed models for the putative PCP-encoding genes in cyanobacteria.
The phylogenetic tree of the cyanobacterial 16S rRNA sequences was generated by
Maximum Likelihood analysis in MEGA 5.05 (
Tamura et al., 2011
), using the Jukes-Can-
tor model (
Jukes & Cantor, 1969
) with a gamma-distributed rate of variation across sites.
To assure statistic significance, 1000 bootstraps were used in the computation of each
tree. The number of
pcp
homologues present in each organism is indicated in brackets.
The predicted evolutionary events are also depicted. HGT: horizontal gene transfer; LCA:
last common ancestor.
17 and the sequences that appear interspersed within the other cyanobac-
terial PCP homologues. After the divergence of
Cyanothece
ATCC 51142
and
Cyanothece
sp. CCY 0110, this last strain also acquired a second
pcp
by
HGT, as supported by the high value of bootstrap (97%) of cluster 16, in
which CY0110_27525 is grouped with heterocystous sequences. In addi-
tion, the genomic context of the gene encoding this protein varies consid-
erably compared to that of the
Cyanothece
ATCC 51142 and CCY 0110
sequences comprised in cluster 1. The
Cyanobacterium UCYN-A
possesses
the smallest cyanobacterial genome known to date, and thus, the lack of