Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
the acceptor on which the polymer grows and the exact process by which
the polymer is exported are yet to be identified (
Cuthbertson et al., 2010
).
On the other hand, the Wzy- and ABC-dependent pathways involve the
participation of a lipid acceptor upon which the polysaccharide is built
(
Cuthbertson et al., 2010
;
Geremia & Rinaudo, 2005
). Both pathways are
well-characterized and can be found in representative serotypes of
Esch-
erichia coli
. As a consequence, the capsule assembly mechanisms of
E. coli
are
regarded as paradigms for EPS assembly in a wide range of bacteria (
Cuthb-
ertson, Mainprize, Naismith, & Whitfield, 2009
;
Steenbergen & Vimr, 2008
;
Whitfield, 2006
;
Whitfield & Paiment, 2003
;
Whitfield & Roberts, 1999
).
These two processes are briefly described below.
2.1. Wzy-Dependent Pathway
The assembly and export of
E. coli
group 1 capsules constitutes the most
well-studied example of the Wzy-dependent pathway (
Fig. 7.1
A). This
process begins with the sequential transfer of the cytosolic nucleotide
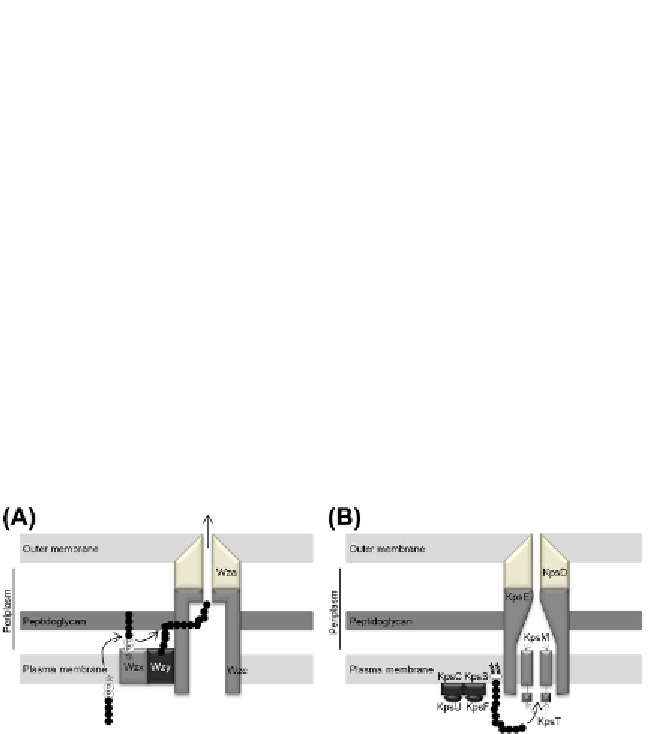
Figure 7.1
Schematic representation of the Wzy-dependent (A) and ABC-dependent
(B) EPS assembly and export pathways. The Wzy-dependent pathway (A) begins with
the assembly of oligosaccharide lipid-linked repeating units at the interface of the cyto-
plasm and the plasma membrane. Subsequently, the repeating units are translocated
to the periplasmatic side of the plasma membrane by the integral protein Wzx, and
polymerized by Wzy. The polymerization reaction is influenced by the activity of the
polysaccharide copolymerase (PCP) protein Wzc, which forms a complex with the poly-
saccharide export (OPX) protein Wza that allows the export of the polymer. In the ABC-
dependent pathway (B), the polysaccharide is fully polymerized in the cytoplasmatic
face of the plasma membrane before being translocated through the plasma mem-
brane by an ABC transporter comprising two transmembrane domains (KpsM) and two
nucleotide-binding domains (KpsT). The participation of KpsC, KpsS, KpsF, and KpsU in
this process is still unclear. The export of the polymer through the periplasm and outer
membrane is performed by the PCP protein KpsE and the OPX protein KpsD (analogous
to the Wzy-dependent pathway) (
Cuthbertson et al., 2009
,
2010
;
Whitfield, 2006
). For
colour version of this igure, the reader is referred to the online version of this topic.