Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
DelValle, & Hanessian, 2008
). All aeruginosins bear a common motif, the
2-carboxy-6-hydroxyoctahydroindole (Choi) residue, with variable residues
at the N- and C-terminal ends, and diverse substituents on the phenyl ring,
and on the Choi residue (
Fig. 6.10
). The biosynthetic genes for aeruginosins
were identified by amplifying NRPS genes using a degenerate PCR approach,
in
P. agardhii
(
Ishida et al., 2007
). The function of the identified genes was
then confirmed by insertional genetic inactivation. The entire gene cluster,
aer
, was then obtained and sequenced in
P. agardhii
NIVA-CYA 126-8 (
Ishida
et al., 2007
) and subsequently in diverse
Microcystis
and
Planktothrix
strains
(
Ishida et al., 2009
;
Rounge et al., 2009
). The
aer
clusters contain the com-
mon
aerABCDEFGHI
genes while other
aer
genes,
aerJKLMN
, have been
identified in
Microcystis
strains only (
Fig. 6.11
). The
aerCDEF
are believed to
be responsible for the production of the Choi amino acid from prephenate,
and the
aerABGIH
genes are responsible for the biosynthesis of the linear
peptide (
Fig. 6.12
). An interesting aspect in this biosynthesis is the presence of
halogenases responsible for the halogenation of the phenyl ring of the primer,
phenyllactate (
Cadel-Six et al., 2008
). The biosynthesis has been proposed on
bioinformatic grounds and only one step, the AerD-catalysed step, has been
actually studied in vitro (
Mahlstedt, S., Fielding, E. N., Moore, B. S., & Walsh,
C. T., 2010
). There are, thus, many uncertainties and, in particular, the releas-
ing step from the PKS AerG, which does not contain any TE domain.
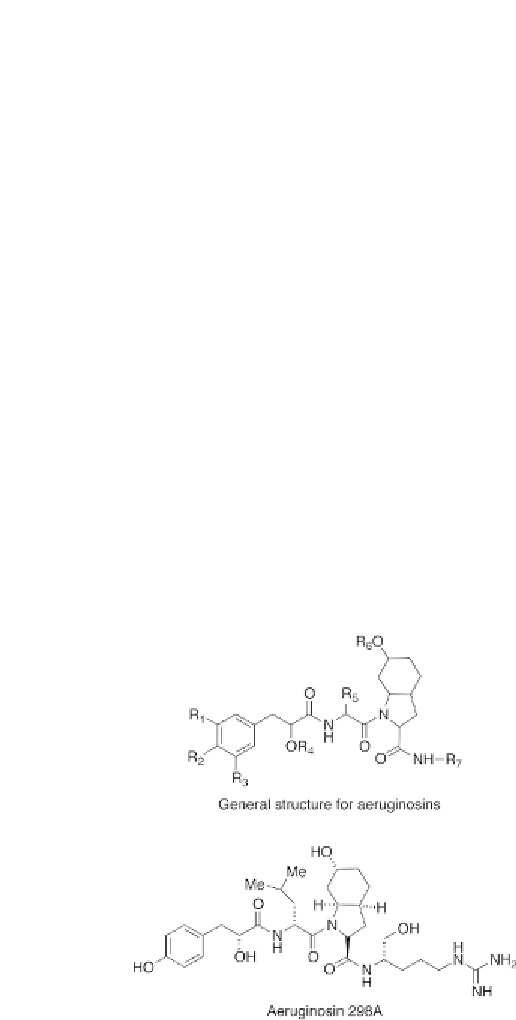
Figure 6.10
Genericstructureforaeruginosinsandthestructureofaeruginosin298A.
Thevariablegroupsare:R
1
andR
2
= H,Cl;R
3
= H,OH,OSO
3
H;R
4
= H,SO
3
H,R
5
= Leu,
Ile,Phe,Tyr,Hty;R
6
= H,SO
3
H,xylose;R
7
= diverseguanidines(see
Ersmark,DelValle,&
Hanessian,2008
).