Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
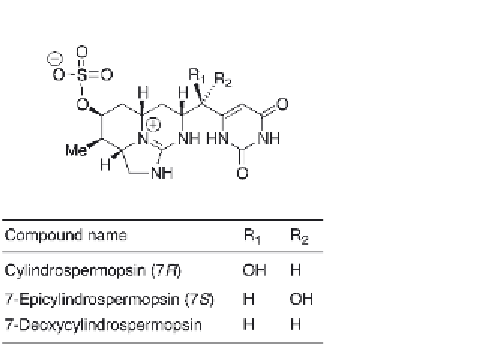
Figure 6.7
Thestructureofcylindrospermopsinanditsnaturalanalogues.
starter of these PKSs was guanidinoacetate (
Burgoyne, Hemscheidt, Moore,
& Runnegar, 2000
). Using degenerate primers to amplify KS domains of
PKSs, Kaplan et al. identified an 11-kb fragment containing three adjacent
genes, including the
aoaA
(equivalent to
cyrA
) gene coding for the putative
amidinotransferase, in
Aphanizomenon ovalisporum
, a cylindrospermopsin pro-
ducer (
Shalev-Alon, Sukenik, Livnah, Schwarz, & Kaplan, 2002
). Later on,
using gene walking technology, Neilan et al. sequenced the entire
cyr
cluster
from
C. racibosrskii
AWT 205 (
Mihali, Kellmann, Muenchhoff, Barrow, &
Neilan, 2008
). The
cyr
cluster was later identified and sequenced in other
cylindrospermopsin producers:
Aphanizomenon
sp. strain 10E6 (
Stuken &
Jakobsen, 2010
),
Oscillatoria
sp. PCC 6506 (
Mazmouz et al., 2010
), and
Raph-
idiopsis curvata
CHAB1150 (
Jiang et al., 2012
). The four
cyr
clusters share
strong identities but the genes are arranged differently (
Fig. 6.8
). Two genes,
cyrN
and
cyrO
, from
C. raciborskii
were not found in the other clusters and are
thus likely not directly involved in the biosynthesis.
cyrN
codes for an adeny-
lylsulfate kinase and this gene has been found in
Oscillatoria
sp. PCC 6506
genome but not in the
cyr
cluster. This activity is implicated in the formation
of a universal sulphate donor (3′-phosphoadenylyl sulphate) and is likely
not restricted to the biosynthesis of cylindrospermopsin. The
cyrO
gene was
putatively annotated as a regulator gene but its function has not been stud-
ied. While no genetic inactivation experiments were reported to prove the
function of the
cyr
genes, the function of the proteins CyrA and CyrI was
demonstrated in vitro (see below in this section). However, a recent study
described a natural inactivation of
cyrI
by insertion in
R. curvata
. This strain
only produces 7-deoxycylindrospermopsin, validating the function of CyrI.