Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
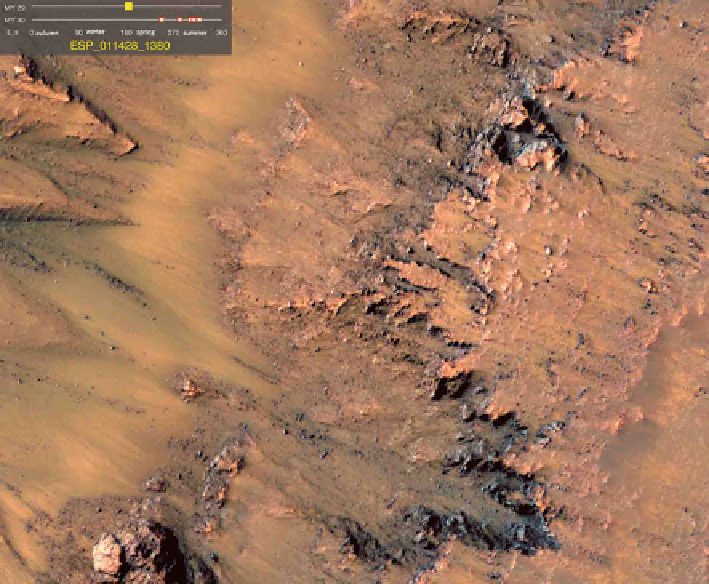
Fig. 8.10
Warm-season flows on the slope of Newton Crater show features that might be evidence
of salty liquid water active on Mars today - Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
(
http://www.nasa.
gov/mission_pages/MRO/multimedia/pia14472.html
- NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona,
2010-2011)
The confirmation that liquid water once flowed on Mars, of the existence of
nutrients, and of the previous discovery of a past magnetic field that protected the
planet from cosmic and solar radiation together strongly suggests that Mars could
have had the environmental factors to support life. To be clear, the finding of past
habitability is not evidence that Martian life has ever actually existed.
When there is a magnetic field, the atmosphere is protected from erosion by solar
wind and it ensures the maintenance of a dense atmosphere, necessary for liquid
water to exist on the surface of Mars.
The two current ecological approaches for predicting the potential habitability
of the Martian surface use 19 or 20 environmental factors, with emphasis on water
availability, temperature, presence of nutrients, an energy source, and protection
from solar ultraviolet and galactic cosmic radiation (MEPAG Special Regions -
Science Analysis et al.
2006
). In particular, the damaging effect of ionizing radiation
on cellular structure is one of the prime limiting factors on the survival of life in
potential astrobiological habitats. Even at a depth of 2 m beneath the surface, any
microbes would likely be dormant, cryopreserved by the current freezing conditions,
and so metabolically inactive and unable to repair cellular degradation as it occurs.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search