Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
into a GIS and the information used to monitor
the state of the environment to give early
warning of extreme weather events and other
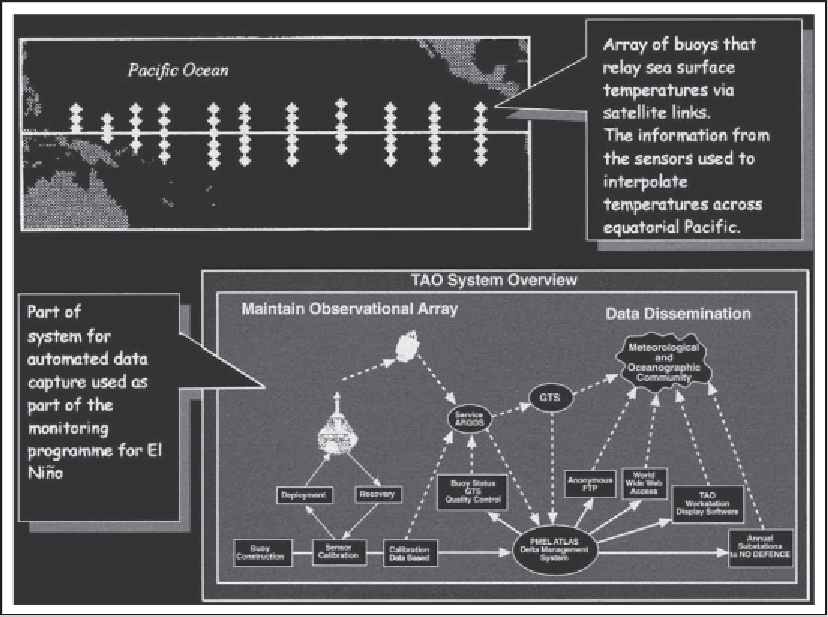
hazards. Figure 40.5 shows part of the system set
up to monitor the El Niño oscillation. It consists
of an array of buoys that record changes in sea
temperatures across the Pacific. This information
is relayed via satellite link back to the monitoring
centre for processing. As we will see later, the
information is used to monitor the dynamics of
the atmosphere-ocean system in the area and to
give warning of the occurrence of an El Niño
event.
A particularly important recent development in
the area of automated data capture has been the
use of the Navstar GPS to record the spatial
location of objects (see additional information).
The GPS system consists of a constellation of
satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites
broadcast radio signals that can be picked up by
GPS receivers on the ground and the information
used to locate the position of the receiver with
accuracies down to a few millimetres, depending
on the equipment and methods used. The location
is fixed by using the information from three or
more satellites to triangulate the position of the
receiver. The positional information is usually
stored by the field worker using a small data logger,
and the information is later downloaded into a
database back in the laboratory.
The availability of GPS not only enables the
more accurate recording of survey information in
Figure 40.5
Array of buoys used to monitor sea temperatures across the Pacific Ocean.
Source:
TAO Project. Acknowledgements to TAO Project Office, Director Dr Michael J.McPhaden.