Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
taxation policies favouring lead-free petrol.
However, such changes have not yet occurred in
many cities of lower latitudes, where children
remain at risk.
Air pollution arising from particulates and
oxides of nitrogen emissions from motor vehicles
is most severe in cities with stable, dry
anticyclonic weather conditions for large parts of
the year, such as Los Angeles, Athens, Tehran and
Mexico City, where it produces photochemical
smog and high concentrations of low-level
atmospheric ozone. In Britain, such smogs may
occur during infrequent stable atmospheric
conditions in both summer and winter. In
Athens, Paris and Mexico City, their incidence
has been so severe that restrictions on the use of
motor vehicles are imposed. Under extreme
circumstances, especially in Mexico City,
factories are asked to reduce or halt production
until atmospheric pollutant levels decrease.
Geographers in Sydney, Australia, and Los
Angeles have traced the diurnal migration of the
Box 9.1
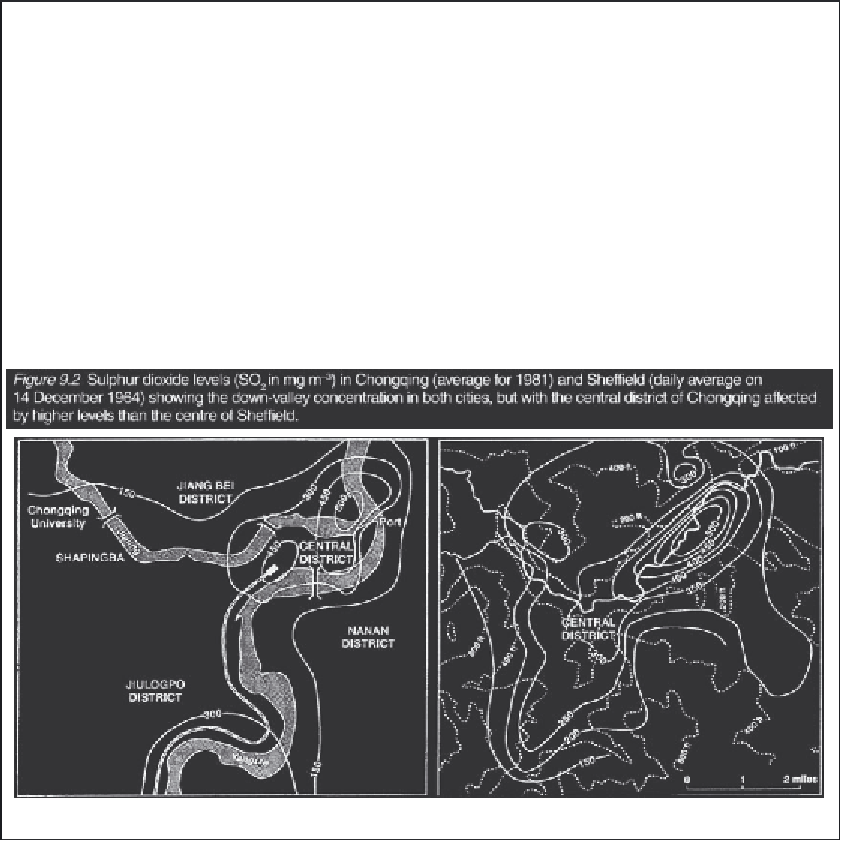
Air pollution by smoke and sulphur dioxide in Sheffield, UK, in the 1950s and 1960s;
and Chongqing, China, in the 1980s and 1990s
Alice Garnett's fine air pollution studies (1967) in
Sheffield in the 1950s and 1960s showed that the heavy
steel industries along the Don valley downstream of the
city emitted waste heat equivalent to approximately 20
per cent of the incoming solar radiation and released
sulphur at rates exceeding 1000 t km2 y
-1
. Atmospheric
SO
2
concentrations often reached levels of 1500 µg m
-3
in the industrial area but fluctuated widely with weather
conditions.
In China, where coal remains a prime source of
energy, the city of Chongqing has severe SO
2
pollution
affecting 2.5 million people along the Jialin and Yangtze
Rivers (Figure 9.2). Major steelworks and heavy
engineering plants emit smoke, which moves down valley
towards the city centre and cannot disperse because of
the overhead inversion layers and fogs, which occur
naturally. Chongqing has the highest SO
2
levels of sixty
Chinese cities and rainfall pH averaging 4.1, producing
acid rain, which causes severe corrosion of many metal
structures in the city. Domestic emissions will fall as
natural gas replaces coal briquettes in cooking stoves,
but factory emissions will continue, while inland
Chongqing fares less well than coastal cities in China's
economic expansion.
In both Sheffield and Chongqing, topography and
their regional situation play a role in determining the
location of the most severe air pollution. In planning the
location of industries, or traffic concentrations with high
emissions, the relief and regional climate must always
be considered if the most severe pollutant concentrations
are to be avoided.
Source:
Chongqing University, and Garnett 1967.