Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
OH
OH
HO
O
O
OH
OH
O
OH
HO
OH
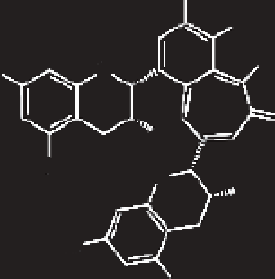
FIGURE 13.10
Chemical structures of the theaflavins found mostly in black tea.
polyphenols in green tea include flavanols and their glycosides, caffeine, small
amounts of methylxanthines, and the amino acid theanine.
Polyphenols in green tea have been identified as strong antioxidants and they pos-
sess anticarcinogenic properties. Human studies on the pharmacokinetics of these
polyphenols suggest that these ingested compounds and their metabolites may play a
role in the action against gastrointestinal cancers.
Many
in vitro
and
in vivo
studies demonstrate that the polyphenols from green
tea are anticarcinogenic by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting cell growth. Probable
action mechanisms include antioxidant and free-radical scavenging activity and
stimulation of detoxification systems through selective induction or modification of
phase I and II metabolic enzymes.
13.9.3 t
heaflaVinS
Theaflavins (Figure 13.10) are antioxidant polyphenols not found in green tea but
present in black tea after the oxidative process. They are formed from the flavan-3-
ols (EGCg) in green tea leaves during the enzymatic oxidation of the tea leaves, thus
imparting the black tea color and flavor. Theaflavin-3-gallate, theaflavin-3′-gallate,
and theaflavin-3-3′digallate are all types of thearubigins, which are reddish in color.
SUMMARY
Natural products are found in foods, spices, and beverages. Natural products are
also used as preservatives for foods (spices) and as sweeteners. Examples include the
important natural sweeteners: stevia, licorice, and agave, followed by examples of
chemicals in spices and the polyphenolics in teas. Teas have had an important role
during human civilization for more than 5000 years.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search