Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
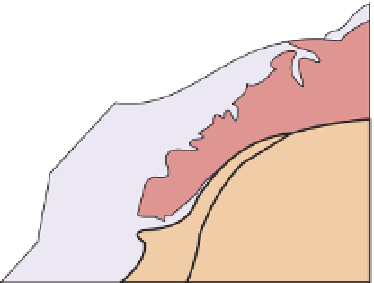
Figure 11.7
The Swiss-Italian sector of the
Western Alps.
A.
Simplified map (based on
Ramsay, 1963) and (
B
) NW-SE generalised
cross-section (modified from Debelmas
30km
molasse
(foredeep
basin)
Helvetic
zone
3
5
AM
11
et
folded
Jura
2
al.
, 1983) showing the main tectonic zones
and their characteristic structural styles;
map: BM, Belledonne massif; AR, Aiguilles
Rouges massif; AM, Aar massif; MB, Mont
Blanc massif; SB, Sub-Briançonnais zone; BZ,
Briançonnais zone; PZ, Piémont zone; DB,
Dent Blanche nappe; MR Monte Rosa massif;
SLZ, Sesia Lanzo zone; section: WN, Wildhorn
nappe; DN, Diableret nappe; MN, Morcles
nappe; SBN, St. Bernard nappe; MRN, Monte
Rosa nappe; IF, Insubric fault.
4
Pre-Alps
Lac Leman
PZ
92
93
Locarno
7
BZ
AR
12
11
MR
9
Southern
Alps
Helvetic
zone
Ivrea
zone
1
MB
DB
13
10
8
Po
basin
BM
PZ
PJ
SLZ
A
6
European plate
African plate
Ivrea, Sesia
Lanzo zones
platform cover
PZ
Piemont zone
SLZ
European crystalline
basement
Southern Alps
Helvetic nappes
molasse/
foredeep basin
Brianconnais
zones
SB, BZ
zone boundaries
SE
2
3
4
5
6, 7
8
10, 11
12
13
NW
Ivrea
zone
Dent
Blanche
nappe
Brian-
connais
zones
Helvetic zone
9
Piemont zone
folded
Jura
molasse
(foredeep basin)
Pre-Alps
Po
basin
Sn.
Alps
SLZ
WN
MN
MRN
DN
SBN
African
basement
European basement
IF
ophiolite
sz
foreland fold-thrust belt
B
sz
20km
ductile nappes and shear zones (sz)
foreland overfold-thrust belt
5. The opening of new oceanic crust
in the western Mediterranean (the
Balearic and Tyrhennian basins after the
main Alpine event (Pliocene to Present)
as Europe rotates anticlockwise.
Tectonic framework of the Western
Alps
Figure 11.7 shows a simplified map of
part of the Western Alps (
see
Figure 11.5
for location) in the NE-SW-trending
section encompassing the Swiss Alps,
which is the most complex tectoni-
cally and contains most of the highest
peaks. This region is usually divided
into 13 tectonic zones; these are as
follows, described from west to east.






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search