Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
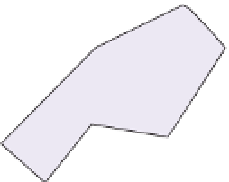
Figure 12.5
Simplified
reconstruction of the tectonic
zones of the Caledonides of
the North Atlantic region after
restoring the effect of Atlantic
opening. Note the major
NW-directed thrusts (red dashed
lines) north of the Iapetus suture
and the SE-directed thrusts
south of the suture; major
strike-slip faults are shown as
solid red lines. The Ordovician
arc terranes north of the suture
are represented in Scotland
only in Shetland.
Ordovician-Silurian
accretionary prism
Laurentia
12
East
Greenland
Ordovician arc terranes
S of suture
Baltica
major fault
major thrust
Welsh basin
Avalonia
?
104
105
foreland
thrust belt
(Scandinavia)
Metamorphic core zone
?
Ordovician arc terranes
N of suture
ophiolites
U
SD
?
Norway
Labrador
Laurentia
plate
MT
, Moine
NH
Scotland
Baltica
plate
Thrust;
GGF
, Great Glen fault;
HBF
HBF
, Highland Boundary fault;
GH
MV
NH
, Northern Highlands;
GH
,
Grampian Highlands;
U
, Unst
SU
?
ophiolite;
MV
, Midland Valley;
Sweden
IS
WB
, Welsh Basin;
IS
, Iapetus
IS
Ireland
suture;
, Tornquist line; DK,
Denmark; SD, Shetland. Based
on a reconstruction by Dewey
and Shackleton (1984).
TQL
?
DK
New-
found
land
WB
Avalonia
England
100km
Netherlands
is a result of the movements on the
Great Glen Fault, which have juxta-
posed terranes that were previously
far to the south-west, away from the
influence of the Scandian collision.
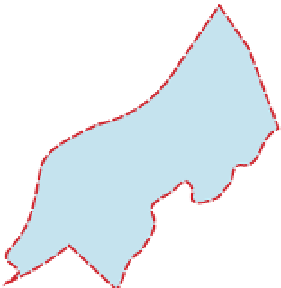
Figure 12.6
Possible arrangement of the continents
of Laurentia, Amazonia and Baltica (part of the
supercontinent of Rodinia) at ~990 Ma showing how
collision with Amazonia may be responsible for the
Grenville orogeny. Modified after a reconstruction by
Pisarevsky
LAURENTIA
et al
. (2003).
Hudson
Bay
The Grenville belt
The
Grenville orogenic belt
extends
from Labrador in north-eastern Canada
along the south-eastern side of North
America as far south as Texas, but is
best preserved in Canada, where it is
known as the Grenville Province. It
was formed in mid-Proterozoic times
during the assembly of the
Rodinia
supercontinent (Figure 12.6) as a result
of collision between the early Prote-
rozoic core of Laurentia and another
continental plate or series of terranes,
now removed. The Canadian sector
of the belt is about 2000 km long and
up to 500 km wide (Figure 12.7).
The Grenville belt has been exten-
sively studied, and the Canadian sector
in particular is comparatively well
known - more so than any of the other
belts of the same age. Unfortunately,
however, only the north-western part
of this belt is now accessible, the south-
eastern part being partly obscured by
the younger Appalachian-Caledonian
belt. It is believed that the missing
opposite side of the orogen may be
represented by a Grenville-age zone
Grenville belt
Rockal plateau
North
Scotland
AMAZONIA
BALTICA
Mid-Proterozoic
collision belts
bordering the Precambrian continen-
tal block known as Amazonia, now
forming the core of northern South
America (Figure 12.6). However, the








































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search