Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
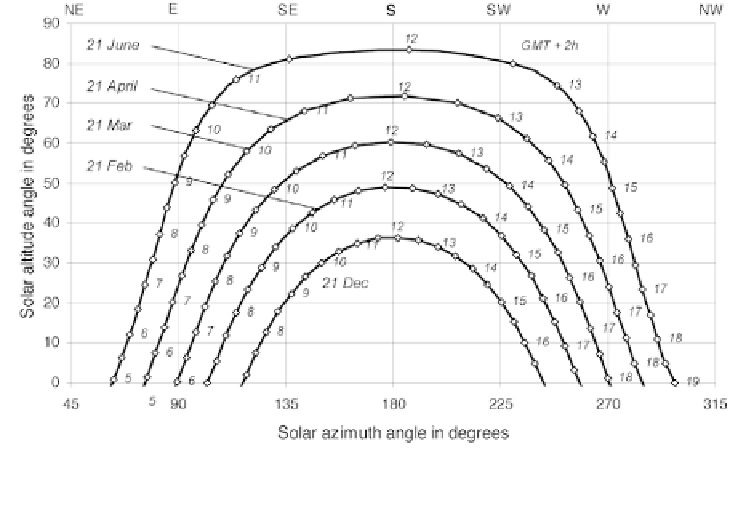
Figure 2.12
Solar Position Diagram for Cairo, Egypt (30.1°N)
C
ALCULATION OF THE
S
OLAR
A
NGLE OF
I
NCIDENCE
The solar angle of incidence
θ
hor
on a horizontal surface is a direct function of
the sun height
γ
S
. This angle is also called the
zenith angle
θ
Z
:
θ
hor
=
θ
Z
= 90° -
γ
S
(2.21)
The calculation of the angle of incidence
θ
tilt
on a tilted surface is more
complicated. The surface azimuth angle
α
t
describes the deviation from the
south. If the surface faces to the west,
α
t
is positive. The inclination angle
γ
t
describes the surface tilt or slope of the surface. If the surface is horizontal,
γ
t
is zero. Figure 2.13 visualizes these angles.
The angle of incidence
θ
tilt
is the angle between the vector
s
in the direction
of the sun and the normal vector
n
perpendicular to the surface. The position
of the sun has been defined in spherical coordinates and thus must be
transformed into Cartesian coordinates with the base vectors north, west and
zenith for further calculations. The vectors
s
and
n
become:
s
= (cos
α
S
•
cos
γ
S
, - sin
α
S
•
cos
γ
S
, sin
γ
S
)
T
(2.22)
γ
t
)
T
n
= (-cos
α
t
•
sin
γ
t
, sin
α
t
•
sin
γ
t
, cos
(2.23)
Both vectors are normalized, and thus the solar angle of incidence
θ
tilt
on a
tilted surface is obtained by calculating the scalar multiplication of these two
vectors: