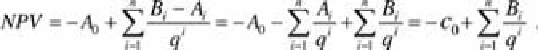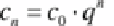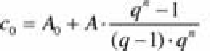Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
In other words, if 6 per cent interest is paid on
€
838 over 25 years, the final
capital is the same as if
€
1500 was invested after 10 years, bearing 6 per cent
interest over 15 years.
The following equation provides the
discounting
of several such payments
at different times:
(6.9)
If the payments
A
i
in the different years
i
are all the same, it becomes:
(6.10)
Then, the capital after
n
years can be calculated again with the equation for
compound interest:
(6.11)
When investing in technical systems for energy conversion, there is likely to be
little capital left that can be repaid after the end of its operating life in n years.
On the contrary, most end-of-life systems are in a poor state of repair and
therefore worthless. Selling the converted energy of the system yields income
for the repayments of the invested capital during the operating time. Hence, it
is now possible to calculate the price at which a unit of energy must be sold so
that the investor gets the required rate of interest.
The sales return also yields interest. If the investor gets a repayment as
early as the beginning of the first operating year, he can reinvest this amount
with payments of interest over the whole operating time. The interest period
decreases for later repayments. The initial capital
c
0
is calculated as described
above with the initial payment
A
0
and the payments
A
i
in the following years
discounted to the initial year. These payments are compared with the income
B
i
. They must also be discounted to the initial year. For simplification,
payments and income within a year are treated as if they were made at the end
of the year. For an operating period of
n
years the calculations become:
(6.12)
NPV
is called the
net present value
; it must be greater than or equal to zero if
the investment is not to yield losses.
In the following, it is assumed that the income
B
at the end of each year is
the same. The size of the required annual income can be estimated if the
equation of the net present value is solved for
B
and the
NPV
is set to zero.
With the annuity factor,
a
, and: