Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
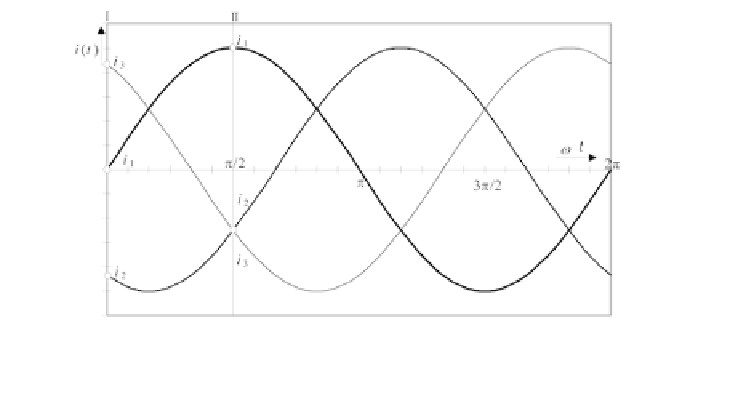
Figure 5.20
Change in the Magnetic Field at Two Different Points in Time
(Stage I and Stage II) when Supplying Three Sinusoidal Currents that are
Temporally Staggered by 120°
frequency of
f
= 50 Hz, the synchronous speed
n
S
, i.e. the speed of the
rotating magnetic field, is
n
S
=50s
-1
= 3000 min
-1
. For a frequency
p
of 60
Hz,
n
s
becomes 3600 min
-1
.
The magnetic field of the stator with three-phase windings in Figure 5.20
has only two poles N and S, i.e. it has one pole pair (
p
= 1). Stators and
windings can also be produced with more pole pairs. When doubling the pole
pairs the rotational speed halves if the mains frequency remains constant. The
mains frequency
f
and the pole pair number
p
define the
synchronous speed
:
(5.67)
The pole pitch can be calculated with the pole pair number
p
and the diameter
d
of the stator:
(5.68)
Figure 5.21 Three-phase Currents to Generate a Rotating Field