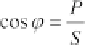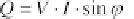Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
power is also available at other phase angles. This power is called
reactive
power Q
and is estimated by:
(5.61)
The reactive power
Q
is positive for positive phase angles. It is then called
lagging reactive power. If the phase angle and the reactive power are negative, it
is called leading reactive power. Sometimes a different definition for the relation
between currents and voltages is used where the phase angle changes by 180°
and therefore all the signs change as well. This can cause some confusion.
The so-called apparent power is defined as:
and
(5.62)
The unit of the active power
P
is W (Watts). The unit of the reactive and
apparent power is also the product of the units of voltage and current. To
avoid confusion and to distinguish between the three power types, other units
are defined for the reactive and apparent power. The reactive power
Q
is
expressed by the unit var (Volt Ampere reactive) and the apparent power
S
with the unit VA (Volt Ampere).
The
power factor
(5.63)
describes the ratio of the active power
P
to the apparent power
S
. Since the
cosine of negative and positive phase angles provides the same value, the power
factor is annotated with the supplemental labels 'inductive' or 'capacitive' in
many cases. This indicates clearly if the phase angle is positive or negative.
Rotating field
If an electric current flows through a wire, it causes a magnetic field
H
as
shown in Figure 5.18 for a wire and a coil.
The magnetic field strength
H
at a distance
r
from an active wire with
electric current
I
is:
Figure 5.18
Magnetic Fields
H
Produced by an Electric Current in a
Wire and Coil