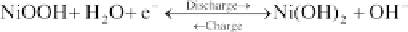Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The nominal voltage of a NiCd cell of 1.2 V is lower than that of a lead-acid
battery cell. NiCd batteries are mainly used as household batteries as well as
for laptops or electric cars.
One major disadvantage of NiCd batteries is the use of environmentally
problematic materials. It surely cannot be avoided that constituent materials
of disposed batteries are released into the environment after the end of the
battery's useful life. Cadmium accumulates in the food chain, and in human
bodies, because it is excreted only partially. High cadmium contamination can
cause organ damage or cancer.
Nickel-metal hydride
(NiMH) batteries are much less environmentally
problematic. Applicable metals are nickel, titanium, vanadium, zirconium or
chrome alloys. However, small amounts of toxic materials are also used for
these batteries. The electrolyte is diluted potash lye, the same as for NiCd
batteries. Besides good environmental compatibility, NiMH batteries have
further advantages compared to NiCd batteries such as higher energy density
and the absence of the memory effect. Disadvantages are the smaller
temperature range and the high self-discharge rate (about 1 per cent per day).
Since the cell voltage of 1.2 V is the same as for NiCd batteries, NiMH
batteries can easily replace NiCd batteries.
The chemical reactions in NiMH batteries are:
Negative electrode:
(4.101)
Positive electrode:
(4.102)
Net reaction:
(4.103)
Estimation of the state of charge for NiCd and NiMH batteries is more
complicated compared with lead-acid batteries. The temperature influence is
greater and the voltage of a fully charged NiCd or NiMH battery even
decreases a little.
Other rechargeable battery types such as sodium-sulphur (
NaS
) batteries
promise advantages of higher energy densities; however, problems with high
operating temperatures and dangerous materials such as sodium have not yet
been resolved fully. Because only prototypes of these batteries exist, they are
not discussed in detail.
Battery systems
The simplest battery system consists only of a photovoltaic generator, a battery
and a load. Since the internal resistance of the photovoltaic generator is very
small, the battery discharges through the photovoltaic generator if the solar
irradiance is low. A
blocking diode
between the photovoltaic generator and
the battery, as shown in Figure 4.45, can avoid these reverse currents from the
battery to the photovoltaic generator; however, this diode causes permanent
losses: