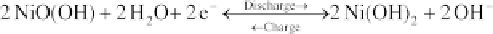Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
R
CC0
,
C
A
= 20-50 F,
C
R
=20
kF. However, these parameters can vary a lot between different battery types.
Much simpler models are used for most simulations. The Gretsch
equivalent circuit can be simplified by ignoring
C
P
,
R
P
and
L
and unifying
R
DC
and
R
CC
as well as
R
DD
and
R
CD
. For long-term considerations, the capacitance
C
A
can be ignored as well.
Charge balancing offers another simple method to describe rechargeable
battery behaviour. Here, a limited number of features is sufficient. If the
battery is full, further charging is not possible; an empty battery cannot be
discharged any further. The charge efficiency must be considered when
charging and discharging a battery. Finally, self-discharge losses must be
considered. Most simulation programs use simple charge balancing methods
to get fast and adequate results.
= 140 m
Ω
,
R
DD0
= 40 m
Ω
,
R
CD0
=40m
Ω
Other rechargeable batteries
Other more expensive rechargeable battery types such as NiCd or NiMH are
used in addition to the lead-acid battery. They have the advantages of higher
energy density, fast charging capability and longer lifetime.
Nickel-cadmium
(NiCd)
batteries
have the following advantages
compared with lead-acid batteries:
•
higher cycle number
•
larger temperature range
•
possibility of higher charge and discharge currents
•
fewer problems with deep discharge.
On the other hand, NiCd batteries have the disadvantages of higher costs and
the so-called
memory effect
. If charging of a NiCd battery is stopped before
the full capacity is reached, the capacity decreases. Repeated full charging and
discharging partly counteracts the capacity reduction; however, the memory
effect is one of the most important problems for this type of battery.
Materials used in the production of NiCd batteries are the metals nickel
and cadmium. The electrolyte is diluted potash lye with a density of between
1.24 kg/litre and 1.34 kg/litre. The chemical reactions in NiCd batteries are:
Negative electrode:
(4.98)
Positive electrode:
(4.99)
Net reaction:
(4.100)