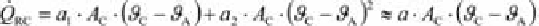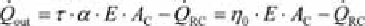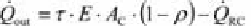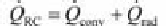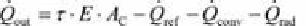Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(3.13)
The convection losses
Q
•
conv
and heat radiation losses
Q
•
rad
can be combined as
Q
•
RC
. The heat radiation losses
Q
•
rad
of selective absorbers are much lower than
the radiation losses of non-selective absorbers as described above. A vacuum
between the front cover and the absorber can reduce the convection losses
Q
•
conv
as described for the evacuated flat-plate and tube collector. The reflection
losses
Q
•
ref
can be estimated using the reflectance
ρ
from the irradiance passing
the glass front cover.
With
and
and the collector power output becomes:
(3.14)
Using the absorptance
α
= 1 -
ρ
of the absorber, the equation reduces to:
(3.15)
with
(3.16)
η
0
is called the
optical efficiency
. It describes the collector efficiency without
any losses due to convection or heat radiation. This is only the case if the
absorber temperature is equal to the ambient temperature.
The thermal losses
Q
RC
depend on the collector temperature
ϑ
C
and the
ambient temperature
ϑ
A
as well as on the coefficients
a
, respectively,
a
1
and
a
2
:
(3.17)
Table 3.7 shows the optical efficiencies
η
0
as well as the loss coefficients
a
1
and
a
2
for various collectors. The loss coefficients of evacuated tube collectors
are much lower than those of non-evacuated flat-plate collectors, hence their
higher efficiency at low ambient temperatures or low irradiances. The loss
coefficients are usually estimated from collector tests. Some calculations only
use the single loss coefficient
a
instead of the two loss coefficients
a
1
and
a
2
.
However, in that case it is not possible to eliminate only
a
2
since that can cause