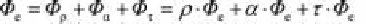Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
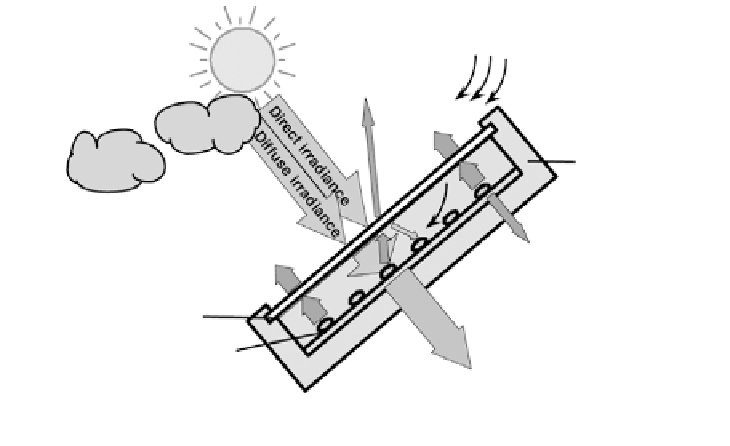
Rain, wind,
snow
Reflection
Convection
Insulation
Heat
radiation
Convection
Glass cover
Absorber
Available
heat
Figure 3.6
Processes in a Flat-plate Collector
can describe these processes. The sum of these three values must always be
equal to one:
(3.7)
The corresponding radiant powers are:
(3.8)
The absorption of the solar radiation heats up the pane of glass. If the glass is
in thermal equilibrium, it must emit the absorbed radiation. Then, the emitted
radiant power
Φ
e
is equal to the absorbed radiant power
Φ
a
, otherwise the
glass would heat up indefinitely. Hence, the emittance
ε
is equal to the
absorptance
α
:
(3.9)
On one hand, the front cover should let through the majority of the solar
radiation. On the other hand, it should also keep back the heat radiation of
the absorber and reduce the convection losses to the environment. Most
collectors use a single glass layer made of thermally treated low-iron solar
glass. This glass has a high transmittance (
1) and a good resistance to the
influences of the environment. Front covers made of glass prevail against those
made of plastic because the lifetime of plastic is limited due to a poorer
resistance to ultraviolet radiation and the influences of weather.
Double glazing
can result in further heat loss reductions but also reduces
the transmitted solar radiant power and increases costs.
τ