Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
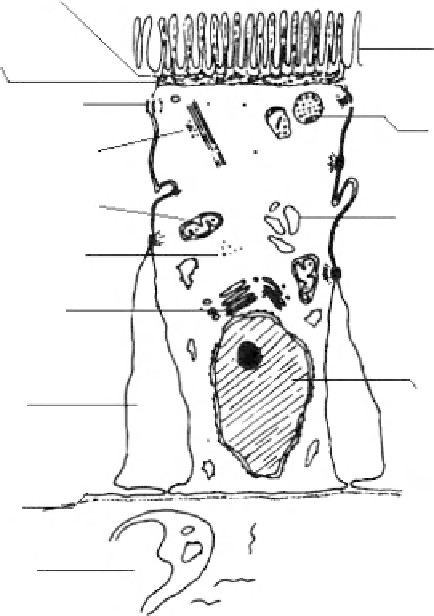
Zonula occludens
Microvilli
Zonula adherens
Macula adherens
Lysosomes
Microtubules
Mitochondria
Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
Free ribosomes
Golgi body
Nucleus
Intercellular space
Basement membrane
Lamina propria
Figure 8.3
Schematic view of the intestinal epithelial absorptive cells.
�.4.�.1.� Microvillus Membrane
The width of the microvillus membrane is 10-11 nm. One of the peculiar features of
this part is the presence of glycocalyx or lubricating glycoprotein on the cell surface.
�.4.�.1.4 Basolateral Membrane
The basolateral membrane of the absorptive epithelial cells differs from the micro-
villus membrane in morphology, biochemical composition, and function. There are
intercellular spaces between adjacent cells. The lateral plasma membranes are about
15-30 nm apart along their entire lengths under conditions of low hydration (net fluid
secretion) but are widened, often to 2 or 3 mm, under conditions of high hydration
(net fluid absorption). The spaces between the adjacent cells is remarkably decreased
by desmosomes—junctions at which adjacent cells attach by thin cytoplasmic pro-
jections. The basolateral membrane of the absorptive cells is directly supported on a
basement membrane.
�.4.�.1.5 Junctional Complexes
Epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa are joined at intercellular attachment
zones, or junctional complexes. The elements of this complex are known as zonula
Search WWH ::

Custom Search