Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
found to be cytotoxic at high concentrations by binding nonspecifically to certain
proteins
[106]
. These induce an antisense effect by an RNase H-dependent mech-
anism
[81,107]
. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides had a half-life of up to 10 h in
human serum compared to only 1 h for an unmodified oligonucleotide of the same
sequence
[108]
, and are taken up by receptor-mediated endocytosis into the cells
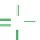
(A)
B
B
O
O
H
H
H
H
H
H
O
P
H
O
P
H
S
-
O
-
O
O
O
O
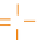
Normal phosphodiester (PO)
Phosphorothioate (PS)
(B)
B
B
O
O
H
H
H
H
H
H
O
H
O
P
O
P
O-CH
3
O
-
O
-
O
O
CH
3
O
O
2'-
O
-methyl RNA (OMe)
2'-
O
-methoxyethyl RNA (MOE)
B
B
B
(C)
O
O
O
O
B
H
H
N
O
O
H
O
-
O
O
NH
P
O
P
O
P
NH
O
-
O
-
O
O
O
O
O
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA)
N3
′
-P5
′
phosphoramidate Locked nucleic acid (LNA)
Hexitol nucleic acid (HNA)
O
B
B
O
O
B
H
N
H
O
P
O
O
P
O
-
O
-
O
O
P
-
O
N
O
O
O
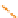
Morpholino
phosphoroamidate (MF)
Cyclohexene
nucleic acid (CeNA)
2
′
-F-arabino
nucleic acid (FANA)
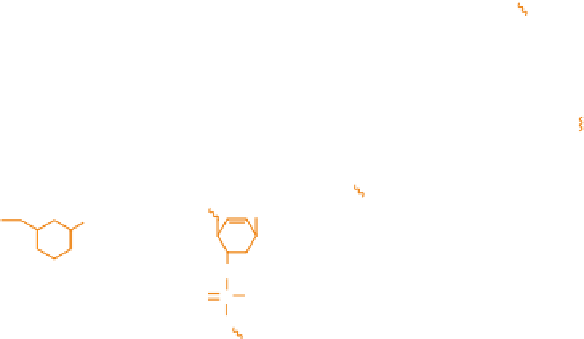
Figure 7.6
Representation of three generations of chemically modified AS ODNs for use in
therapeutics. (A) First-generation AS ODNs. (B) Second-generation antisense ribonucleotides
modified at the 2 hydroxyl by adding a methyl (OMe) or a methoxyethyl (MOE) group.
(C) Third-generation modifications involving a variety of sites including the entire backbone as in
the peptide nucleic acid (PNA), a backbone substitution as in the N3-P5 phosphoroamidate
(PA), the conformational lock in the locked nucleic acid (LNA), or the substituted ring in the
hexitol nucleic acid (HNA) or morpholino phosphoroamidate (MF) or cyclohexene nucleic
acid (CeNA) or 2-F-arabino nucleic acid (FANA).









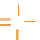






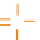





















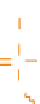












Search WWH ::

Custom Search