Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
18
35
30
50
37
127
125
138
1019
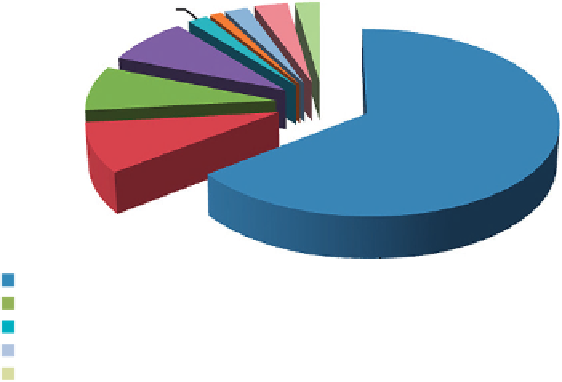
Cancer diseases 64.5% (
n
= 1019)
Cardiovascular diseases 8.7% (
n
= 138)
Monogenetic diseases 7.9% (
n
= 125)
Infectious diseases 8% (
n
= 127)
Ocular diseases 1.1% (
n
= 18)
Gene marking 3.2% (
n
= 50)
Neurological diseases 1.9% (
n
= 30)
Other diseases 2.2% (
n
= 35)
Healthy volunteers 2.3% (
n
= 37)
Figure 6.3
Distribution of diseases targeted by gene therapy.
More than 200 genes have been introduced into cells in human gene therapy trials
using both viral and nonviral vectors
[13]
. The vast majority of gene therapy clinical
trials performed to date are still in phase I or I/ II. The two categories combined rep-
resent 79.2% of all gene therapy trials, 16.3% are phase II trials, and phase II/III and
III trials represent only 4.2%
[13]
.
6.2 DNA Vaccination
Since 1786, when Edward Jenner first used live attenuated vaccination for small
pox, remarkable developments and advancements have resulted in the prevention of
many human infectious diseases like small pox, measles, and rubella. These develop-
ments in vaccination improve the average human life, providing lifelong protection
by induction of immunological memory. The major limitation of these live attenu-
ated vaccines is their failure to control infectious diseases like tuberculosis and HIV,
which has led to a new generation of vaccines known as subunit vaccines. The major
problems associated with traditional live vaccines have already been overcome using
subunit and recombinant protein vaccines. However, the challenge of developing
potent and safe vaccines for diseases like cancer, tuberculosis, and HIV has not been
satisfied.
In 1990, the first report that intramuscular injection of plasmid DNA in saline solu-
tion could transfect muscle cells
in vivo
gave rise to today's DNA vaccines
[14]
. The
study suggested that plasmid DNA could be used to express foreign proteins inside a
cell, and thus could induce an immune response against the expressed proteins. DNA
Search WWH ::

Custom Search