Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
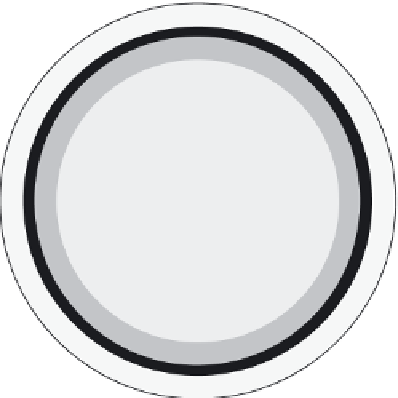
Lipid envelope
RTase
Viral RNA
Capsid core protein
25nm
Receptor-binding proteins
Figure 5.9
Morphology of retrovirus.
The presence of functionally conserved noncoding sequences is also essential for the
viral life cycle. Conserved noncoding sequences are shown in
Table 5.6
.
5.4.2 Design and Construction of the Retrovirus
Retroviral vectors are usually used to induce the production of a specific protein in
transduced cells. A simple approach is to use the promoter in the retroviral LTR to
control the expression of a cDNA encoding the protein of interest. Tissue-specific
expression or inducibility can be provided by the modification in the enhancer/pro-
moter of the LTR. Several ATG start codons are present in the 5-untranslated regions
of commonly used vectors
[151]
. A single coding region can be expressed by using
an internal promoter that also allows more flexibility in promoter selection. These
strategies for expression can most easily be implemented when the gene of interest
is also a selectable marker, which allows facile selection of vector-transduced cells.
The vector can be introduced into packaging cells by cotransfection with a selectable
marker present on a separate plasmid. This strategy has the appealing advantage for
gene therapy that a single protein is expressed in the ultimate target cells with low
toxicity or antigenicity of a selectable marker. When the inserted gene is not select-
able, this strategy has the disadvantage that it is more difficult to generate cells that
produce a high-titer vector stock, and it is more difficult to determine the titer of the
vector.












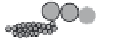



































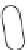



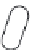




















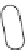




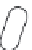












Search WWH ::

Custom Search