Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5
′
3
′
5
′
3
′
5
′
5
′
3
′
5
′
Double strand gap created by exonuclease activity
on 5
′
end of the broken double strand
Single strand 3
′
extensions pair with its
Complementary sequences on the intact homologue
DNA polymerase extends invading 3
′
end and branch
migration creates Holliday intermediates exhibiting
two crossover sites
DNA replication at the missing site is completed
Cleavage of the Holliday intermediate
generates one of the two sets of
recombinant product
Recombinant set 1
Recombinant set 2
Figure 1.5
DNA recombination.
through a very precise mechanism, without any addition or deletion of nucleotides.
This recombination is not site specific and can occur anywhere in the region of simi-
larity, but regions of high probability do exist. Homologous recombination is also
a DNA repair mechanism and is important for maintenance of genetic diversity.
Homologous recombination uses a host of enzymes during the process.
Although homologous recombination is not site specific, recombination can be site
specific and also involves recombination between nonhomologous regions. Enzyme





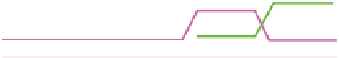

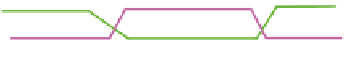




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search