Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Quaternary ammonium
Heterocyclic
Amino acid
Guanidinium
Polyamines (branched,
linear)
Glycerol
phosphonium
Carnitine
Arsenic
Cyclic carbon
Hydrophobic
Scaffold
Head
Ligand
Linker
Linker
Linker
Antibodies
Folate
Transferrin
Peptides
Cholesterol
Fatty acid (1-4)
Vitamin D
Bile acids
Ester carbamate
Ether C1-C5
Disulfide
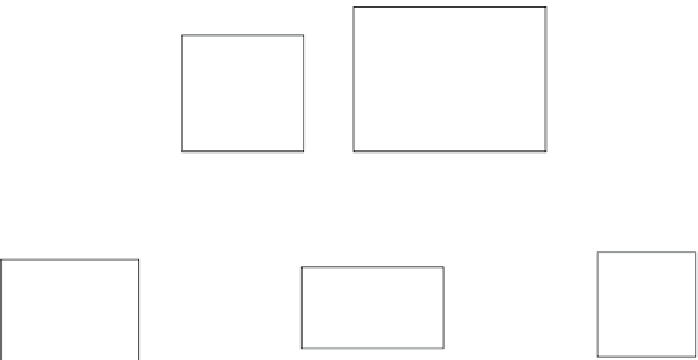
Figure 4.8
A schematic of the various domains of a cationic lipid.
moiety that played the role of maintaining a self-assembling system with DNA and
promoting fusion with the cell membrane. By virtue of its excess positive charges
at the surface of the complexes, cationic lipid DOTMA facilitates adhesion to the
cell membrane. The combination of cationic lipid DOTMA with neutral lipid DOPE
termed as Lipofectin
TM
was described as a liposomal vector by Syntex Inc.
[194]
.
Patent WO9011092 by Vical Inc. described overtly the use of these quaternary
ammonium salt lipids, either alone or in combination with DOPE or DOPC for DNA
delivery.
When diether bonds of DOTMA were replaced by diester bonds, they formed a
biodegradable agent known as (1,2-dioleoyloxy-3-(trimethylammonio) propane chlo-
ride) DOTAP (
Fig. 4.9
), which has been shown to accumulate less in tissues than
DOTMA. The quaternary ammonium salts of DOTMA can be substituted with
alkylene alcohol or alkylene amines and differing lipid chains, to give 1,2-dimyri-
styloxypropyl-3-dimethyl-hydroxyethyl ammonium bromide (DMRIE) and (/-)-
N
-
(3-aminopropyl)-
N
,
N
-dimethyl-2,3-bis(dodecyloxy)-1-propanaminium bromide (DLRIE)
(
Fig. 4.9
). Few compounds of this class have demonstrated a substantial increase in
transfection efficiency and moved successfully to the clinical stage
[195,196]
. To
discover the structural characteristics responsible for high transfection efficiency in
DOTMA, Ren et al. synthesized a series of DOTMA analogues
[197,198]
and con-
cluded that paired oleoyl chains, such as a lipid anchor, attached to the cationic head
group by ether linkage to the 1,2 position of the glycerol backbone, were responsible
for high transfection efficiency. They proposed that
in vitro
transfection activity can
be determined by the structure of lipoplex and the result of the interaction, after IV
administration, between lipoplex and blood components
[199]
.
Attachment of glucose or galactose moiety to enhance cell targeting was pro-
posed, using the concept of receptor-mediated endocytosis
[200]
. In another study, a
lipophilic anchor was inserted with oligo-oxyethylene units at the linkage position of
the hydrophobic tails
[201]
. However, the synthesized compound was not evaluated









Search WWH ::

Custom Search