Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
cells to the solid tumor region. Thus, it increased the survival rate and inhibited
tumor growth after repeated injections of PAGA-IL-12 pDNA complexes
[93]
.
4.2.2 Noncondensing Polymers
4.2.2.1 Poloxamers (Pluronic® Block Copolymers)
Pluronic
®
block copolymers are composed of hydrophilic ethylene oxide (EO) and
hydrophobic propylene oxide (PO) blocks arranged in a basic A-B-A structure:
EOx-POy-EOx (
Fig. 4.7
). BASF Corp. (Parsippany, NJ, USA) manufactures over 30
Pluronic
®
molecules with different lengths of EO (NEO) and PO (NPO) blocks. These
molecules are characterized by different hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) and
critical micelle concentration (CMC). Pluronic
®
block copolymers are synthesized by
sequential addition of PO and EO monomers in the presence of an alkaline catalyst
[94]
. Initially the reaction proceeds with polymerization of the PO block followed by
the growth of EO chains at both ends of the PO block. Highly purified block copoly-
mers are obtained by chromatographic fractionation to remove the presence of admix-
tures, mainly of the PPO homopolymer and block copolymers containing shorter PEO
chains. Unimers, above CMC, individual block copolymer molecules have the tendency
to self-assemble into micelles in aqueous solutions, through a process called micelliza-
tion. The driving force for micellization is the hydrophobic interactions of the PO
blocks. The micelles have a hydrophobic PO core and a hydrophilic EO shell, and their
shape can be spherical, lamellar, or rodlike, depending on the lengths of the PO and EO
chains
[95]
.
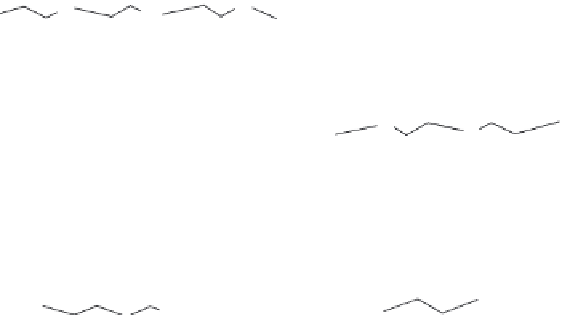
O
O
O
H
HO
n
m
n
PO
EO
EO
O
O
EO: Ethylene oxide
PO: Propylene oxide
O
n
m
z
O
Poloxamer
PLGA
CN
CN
HO
H
n
n
N
O
O
O
O
R
O
R
Poly(alkylcyanoacrylate)
Poly(vinyl pyrolidone)
Figure 4.7
Chemical structures of noncondensing polymers.

















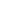
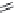
Search WWH ::

Custom Search