Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Social Structure
Undoubtedly, the newly developed microsatellite markers will be invaluable also for the
investigation of the social structure of
Sotalia
dolphins. Besides being highly polymorphic,
microsatellites are useful for that purpose because they are bi-parentally inherited.
During the last decade, many interesting results have been found concerning the social
behaviour of
S. guianensis
, especially through long-term photo-identification studies. Three
local populations in Brazil showed strong residency (North Bay, Santa Catarina - Flores 1999;
Cananéia Estuary, São Paulo - Santos et al., 2001; Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro - Azevedo
et al., 2004), and that pattern may prove to be a feature of that species throughout its
distribution.
In spite of the vast database on social associations built during the long-term monitoring
of some
Sotalia guianensis
populations, studies on social structure have been hampered by
the absence of easily observable sexual dimorphism. Sex determination of free-ranging
Sotalia
relies on the observation of the animal's ventral area, which is a rare event in the field.
Therefore, sexing is only achieved for reproducing females, on the basis of their close, lasting
and recurring association with calves. That approach demands a long-term monitoring of the
population, and does not allow the detection of males and non-reproductive individuals.
Fortunately, remote biopsy darting has been safely and successfully applied to
Sotalia
dolphins, providing samples that can be sexed molecularly. Two genetic systems are usually
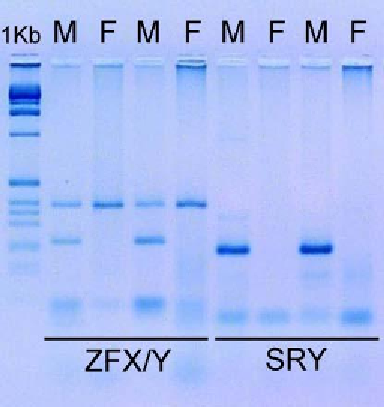
applied for sex determination in cetaceans: the ZFX/ZFY (Bérubé and Palsbøll, 1996) and the
SRY (Palsbøll et al., 1992). Both systems have been tested and optimized for
Sotalia
species,
and have been successfully used for sexing biopsy samples (Cunha and Solé-Cava, 2007)
(Figure 6). Additionally, those molecular techniques allow the sex determination of carcasses
in advanced decaying, when sexing cannot be done by the examination of the genital opening.
Figure 6. Sex determination patterns of
Sotalia
samples using the ZFX/ZFY
and SRY systems. M:
male, F: female, 1Kb: DNA size ladder.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search