Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
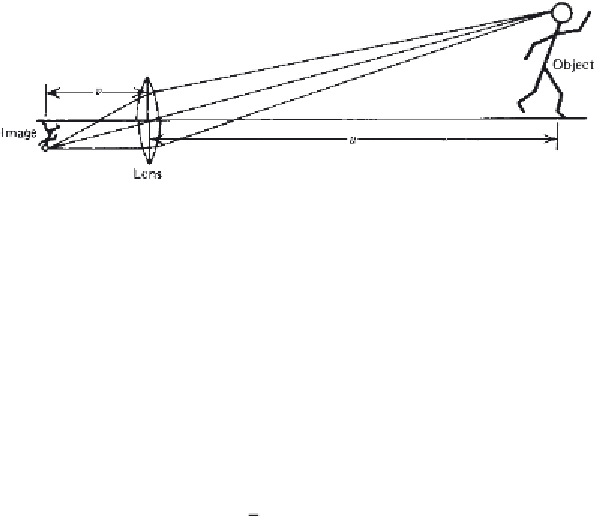
Figure 3.8
Simple focusing lens system showing relationship between the object and
image.
optoelectric types. Whichever system is chosen, a lens is involved; therefore,
a short review of basic optics is given here.
3.3.1 Review of Basic Lens Optics
A simple converging lens is one that creates an inverted image in focus at a
distance
v
from the lens. As seen in Figure 3.8, if the lens — object distance
is
u
, then the focal length
f
of the lens is:
1
f
=
1
v
+
1
u
(3.1)
The imaging systems used for movement studies are such that the object —
lens
distance
is
quite
large
compared
with
the
lens — image
distance.
Therefore,
1
u
≈
1
f
=
1
v
,
=
v
0,
r
f
(3.2)
Thus, if we know the focal length of the lens system, we can see that the
image size is related to the object size by a simple triangulation. A typical
focal length is 25 mm, a wide-angle lens is 13 mm, and a telephoto lens is 150
mm. A zoom lens is just one in which the focal length is infinitely variable
over a given range. Thus, as
L
increases, the focal length must increase
proportionately to produce the same image size. Figure 3.9 illustrates this
principle. For maximum accuracy, it is highly desirable that the image be as
large as possible. Thus, it is advantageous to have a zoom lens rather than
a series of fixed lenses; individual adjustments can be readily made for each
movement to be studied, or even during the course of the event.
3.3.2
f
-Stop Setting and Field of Focus
The amount of light entering the lens is controlled by the lens opening,
which is measured by its
f
-stop (
f
means fraction of lens aperture opening).














Search WWH ::

Custom Search