Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.00
mean
2
s
.10
.01
.001
0
12 34 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
18
19
20
Harmonic Number
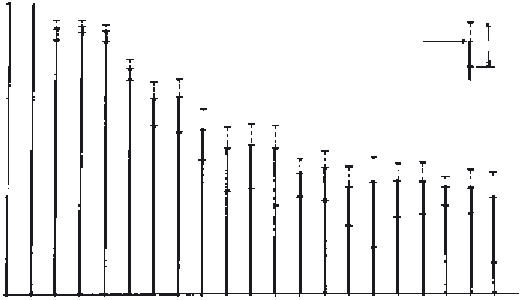
Figure 2.17
Harmonic content of the vertical displacement of a toe marker from
20 subjects during normal walking. Fundamental frequency (harmonic number
1)
is normalized at 1.00. Over 99% of power is contained below the seventh harmonic.
(Reproduced by permission from the
Journal of Biomechanics
.)
=
calculate velocities and accelerations from the displacement data, as will be
evident later in Section 3.4.3.
The theory behind digital filtering (Radar and Gold, 1967) will not be
covered, but the application of low-pass digital filtering will be described in
detail. As a result of the previous discussion for these data on walking, the
cutoff frequency of a digital filter should be set at about 6 Hz. The format
of a recursive digital filter that processes the raw data in time domain is as
follows:
X
1
(nT )
=
a
0
X (nT )
+
a
1
X (nT
−
T )
+
a
2
X (nT
−
2
T )
+
b
1
X
1
(nT
b
2
X
1
(nT
−
T )
+
−
2
T )
(2.18)
where
X
1
=
filtered output coordinates
X
=
unfiltered coordinate data
=
n
th sample
nT
(nT
−
T)
=
(
n
−
1)th sample
(nT
−
2T)
=
(
n
−
2)th sample
a
0
,
...
,
b
0
,
...
=
filter coefficients
These filter coefficients
a
0
,
a
1
,
a
2
,
b
1
and
b
2
are constants that depend on the
type and order of the filter, the sampling frequency, and the cutoff frequency.
As can be seen, the filter output
X
1
(nT)
is a weighted version of the immediate
and past raw data plus a weighted contribution of past filtered output. The









Search WWH ::

Custom Search