Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
n
p
W
:
RX
Æ
by
()
=«.
p
W
pL X
p
The map p
W
is called the
parallel projection of
R
n
onto the plane
X
parallel to
v
. If
v
is
orthogonal to
X
, then p
W
is called the
orthogonal
or
orthographic projection of
R
n
onto
the plane
X
; otherwise, it is called an
oblique parallel projection
. In general, if
X
and
Y
are any subsets of
R
n
, then the map that sends
p
in
X
to
L
p
«
Y
in
Y
(wherever it
is defined) is called the
parallel projection of
X
to
Y
.
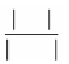
Figure 2.22 shows a parallel projection of a line
L
onto a line
L
¢ and Figure 2.23,
a parallel projection of a plane
X
onto a plane
X
¢. Note that the ratio of distances is
preserved in the case of parallel projections of a line onto another line. What this
means is that, referring to Figure 2.22, the ratio
AB
A
¢¢
is independent of
A
and
B
. This is
not
the case for parallel projections of one plane
onto another. For example, in Figure 2.23 the ratios
L
L¢
B
L
B
A
B¢
L
A
A¢
Figure 2.22.
A parallel projection between
lines.
v
X
B
A
C
X¢
B¢
A¢
C¢
Figure 2.23.
A parallel projection between
planes.