Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
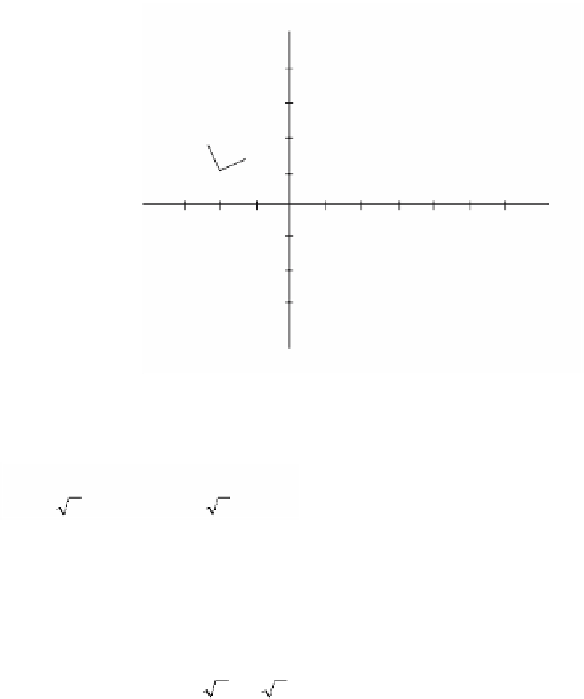
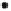
Figure 2.16.
Example 2.2.8.5.
y
C(-2,4)
u
2
B(0,2)
u
1
A(-2,1)
A¢(4,0)
x
u
1
¢
B¢(6,-1)
u
2
¢
C¢(4,-3)
and
1
5
1
5
()
(
)
u
¢=
21
,,
u
¢=
-
12
, .
1
2
Equations (2.22) and (2.21) imply that
2
5
1
5
Ê
ˆ
-
Á
Á
˜
˜
-
1
(
)
=+ -
(
)
Fxy x y
,
21
,
,
1
5
2
5
Ë
¯
2
5
1
5
Ê
ˆ
-
Á
Á
˜
˜
Fxy
¢
(
,
)
=
(
xy
,
)
+¢
A
,
1
5
2
5
-
-
Ë
¯
and
2
5
1
5
2
5
1
5
Ê
ˆ
Ê
ˆ
-
-
Á
Á
˜
˜
Á
Á
˜
˜
(
)
=
(
)
=+ -
(
)
+
(
)
xy
¢¢
,
Mxy
,
x
21
,
y
40
,
.
1
5
2
5
1
5
2
5
-
-
Ë
¯
Ë
¯
This leads to the following equations for M:
xx6
¢=
+
yy1
¢=- +