Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
geometrical relationships, such as the sum of the angles in a triangle always equals
180
°
.
Even though Euclidean geometry is very old and physics has modified its appli-
cability to certain phenomena that are better explained by Einstein's theory of rela-
tivity, quantum dynamics, and so on, Euclidean geometry is very important for many
modern activities ranging from surveying to computer-aided design, computer
vision, and robotics. If you have ever played, or seen, a new videogame and been
amazed by the graphics, a large proportion of the math behind those graphics is
based on Euclidean geometry.
The law of sines is one of the most fundamental parts of Euclidean geometry
used by surveyors. It expresses the relationship between an angle and its opposite
side. In right angle triangles, the sine is the relationship between the opposite side
and the hypotenuse. In any triangle, the ratio of one side to its opposite angle is the
same as the ratio of any other side to its opposite angle. Expressed mathematically:
a
=
b
=
c
Sin A Sin B Sin C
The law of sines is related to the law of cosines and also to the law of tangents.
These are more complicated formulas for solving for the lengths of sides and size of
unknown angles.
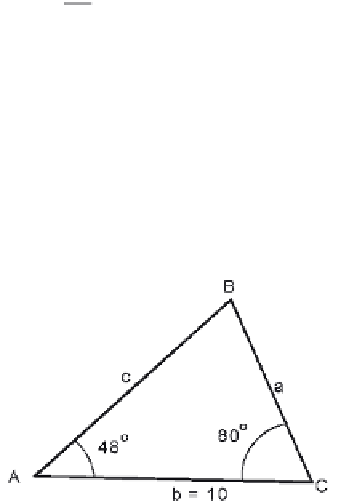
Using the Law of Sines in Surveying
The law of sines is used to solve the length of an unknown side when you know the
length of one side and two angles. In this example, I go through the steps to find out
the length of c in this figure.
In the law of sines, all ratios are equivalent. If we know any three terms from two
ratios, we can use basic algebra to solve for the unknown term. In this case:
a
b
c
=
=
Sin A
Sin B
Sin C
Now substituting the known terms
b
c
=
Sin B
Sin C
then using a sine table or the first three digits of a calculator's sine:
10
=
c
.788 .985




Search WWH ::

Custom Search