Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Hellas and Argyre do not show the remnant
field, the
conditions leading to the magnetic
field must have been
lost prior to the impacts, or before ~4 Ga.
The remnant magnetic
field patterns are very similar to
the bilateral symmetry of Earth
'
s paleomagnetic stripes on
the sea
floor that are indicative of sea-
floor spreading.
Detailed analysis of the martian patterns even suggests
the presence of transform faults to some planetary scien-
tists. Although the MGS data are of low resolution, the
discovery of the remnant
field could mean that Mars had
early in its history a magnetic
field that has since been lost
and that the stripping pattern would be consistent with a
form of plate tectonics.
colleagues (Bibring et al.
2006
), phyllosilicates character-
ize early Mars history, re
ecting the presence of slightly
alkaline liquid water, while younger rocks contain
hydrated sulfates, and the youngest materials consist of
anhydrous iron oxides.
Some of the remote sensing data have been
ground-
truthed
”
by measurements from landed spacecraft and
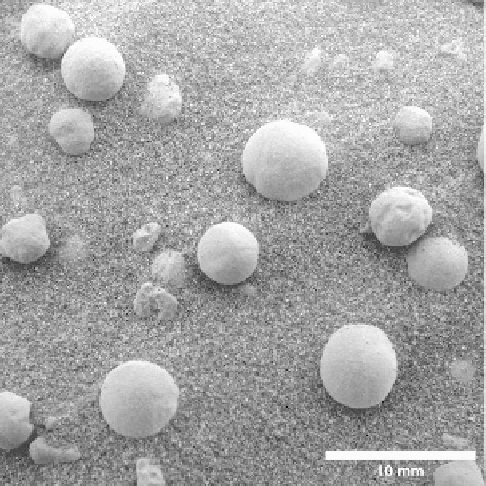
rovers. For example, TES data suggested the occurrence
of crystalline hematite in some areas of Mars. Because this
mineral forms predominantly in the presence of liquid
water, these areas became of high priority for surface
exploration and this resulted in the selection of the
Meridiani Planum landing site for the rover Opportunity.
Subsequent rover data con
rmed the TES observations
through analysis of the hematite
“
blueberries
”
(Fig. 7.3)
.
Similarly, in situ surface data show the dominance of
basaltic compositions and the presence of a suite of chemi-
cally weathered minerals, including sulfates and halides.
Surprisingly, though, there is a general absence of abun-
dant carbonates in the remote sensing and lander data.
While carbonates have been found in some martian mete-
orites and at some sites, they were expected to be rather
common on Mars, given the carbon dioxide atmosphere,
and their relative absence remains a puzzle. The calcium
carbonate detected by Phoenix is thought to have resulted
“
7.4 Surface composition
Information on Mars
surface and near-surface composi-
tions comes mostly from the martian meteorites, remote
sensing, and in situ measurements made from landers and
rovers. More than four dozen meteorites have been found
on Earth that bear the distinctive geochemical
'
”
of Mars when matched against measurements made by
landers. Although these rocks display a wide range of
crystallization ages (4.5 Ga to less than a couple of hundred
million years) and histories, most are of basaltic or similar
ma
c compositions, con
rming earlier interpretations of
multispectral data from Earth-based telescopes.
Global or near-global remote sensing data are available
from orbiters that
flew in the 1990s to early 2000s. The
TES instrument on the MGS (Christensen et al.,
2001
)
mapped mineralogies using the mid-IR part of the electro-
magnetic spectrum
(Fig. 2.14)
and showed that plagio-
clase feldspar, pyroxene, and olivine are common, along
with some limited exposures of high-silica materials, all
consistent with basalts as the primary rocks on the surface.
As noted by TES designer Phil Christensen, the data also
suggested the presence of andesitic materials, although the
data can also be explained by invoking the presence of
primary igneous glass and/or weathered basalts. The
Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) on Mars Odyssey map-
ped elemental compositions and showed that iron concen-
trations are high (as expected for basalts) and relatively
uniform across the surface, while chlorine values vary
substantially.
The near-IR multispectral mappers OMEGA and
CRISM have returned compositional data that can be
correlated with rock units of different ages. As outlined
by French planetary scientist Pierre Bibring and his
“
“fingerprints”
Figure 7.3. A Microscopic Imager view of spherical hematite grains,
called
because of their spectral properties, as seen at
the rover Opportunity landing site (the image covers an area of
31mm by 31mm).
“
blueberries
”