Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
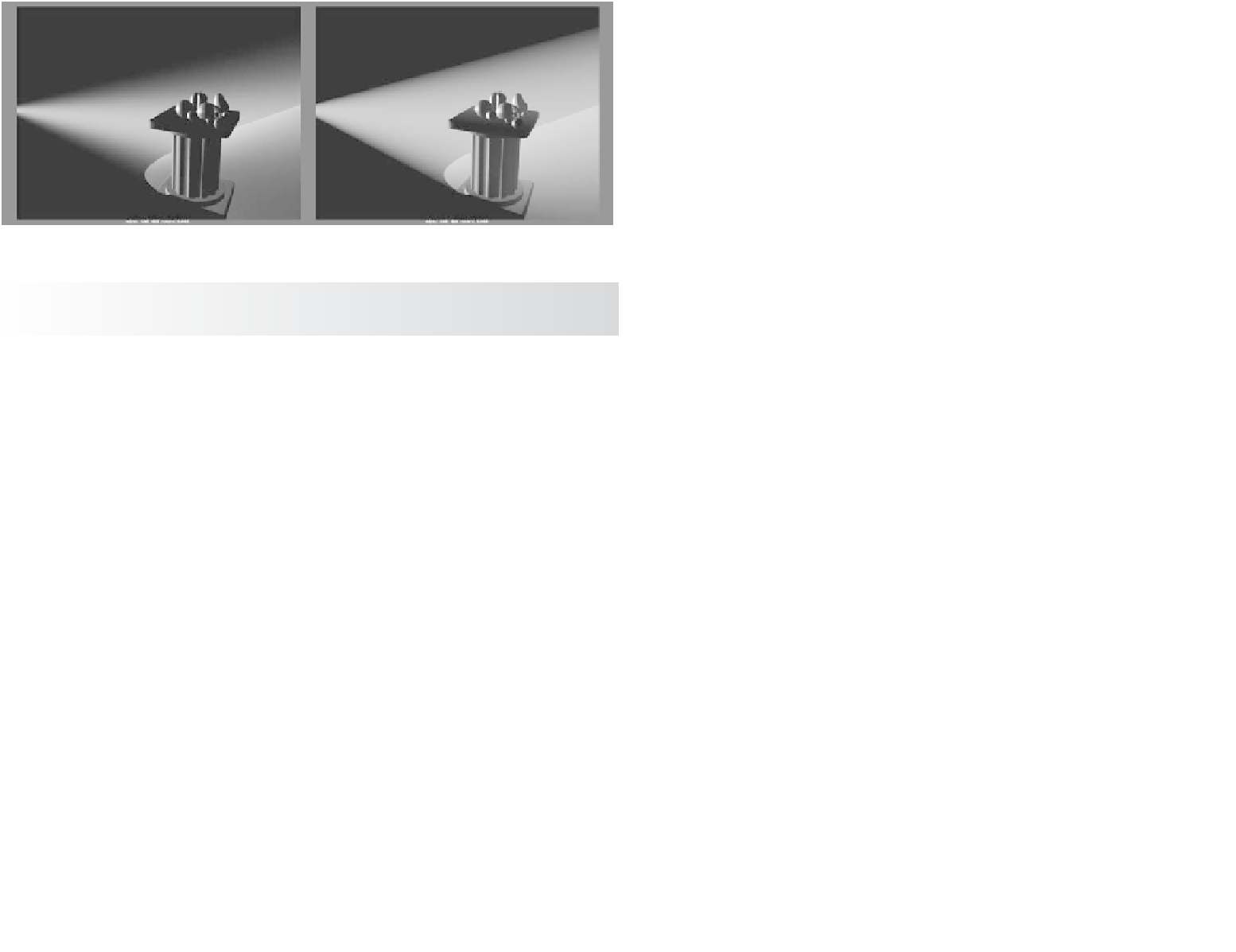
of the fog, and Fog Spread controls how well the fog is defined within its confines. For
example, a Spot light with a fog shows the fog in its cone. Figure 10.52 shows how Fog
Spread affects the conical fog shape.
Figure 10.52
Fog Spread affects
how the fog dis-
sipates to the edges
of the cone.
Fog Spread = 0.5
Fog Spread = 2.0
To remove a fog effect, right-click the Light Fog label in the light's Attribute Editor, and
choose Break Connection from the shortcut menu.
If you want the light fog-cast shadows to make rays of light within the fog, check Use
Depth Map Shadows for the light. You'll have to increase the depth-map Resolution for a
higher-quality image.
Lens Flare
Lens lare
and
light glow,
as illustrated in Figure 10.53, mimic the real-world effect created
when light strikes a lens or when the light source is visible in the frame. The flare is cre-
ated when the light hits the lens at a particular angle and causes a reflection of itself in the
optics of the lens.
Figure 10.53
Light glow and lens
flare turned on for
the back light
To enable a light glow, under the Light Effects section in
the light's Attribute Editor, click the checkered Map but-
ton next to the Light Glow attribute to create an OpticalFX
node that appears in the Hypershade. The Attribute Editor
shifts focus to that new node, which controls the behavior
of the light glow and lens flare. The OpticalFX node con-
tains the following attributes and settings:
Glow Type
Setting this attribute specifies the kind of glow:
Linear, Exponential, Ball, Lens Flare, and Rim Halo. These
define the size and shape of the glow from the light.