Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The base for the cartographical ontology was thesaurus - lexicon of cartographical terms.
The lexicon also contained a list of synonyms. In the dictionary pruning stage, a pair wise
comparison between the cartographic terms and their descriptions result to lexicon set.
Synonyms of terms were grouped together. As a result, one description was chosen to
represent all the synonym terms. The differences between the Central Europe and the
English cartographic school were solved by the decision to design two ontologies - the
Czech ontology and the English ontology. This chapter and figures describes only the
English ontology for the better readability. The main classes are Data, MapColor,
MapComposition, MapDescription, MapSymbol, Method, Phenomenon, Projection,
SymbolVariables and Scale. These cartographic terms are expressed by
classes
in ontology
in OWL language.
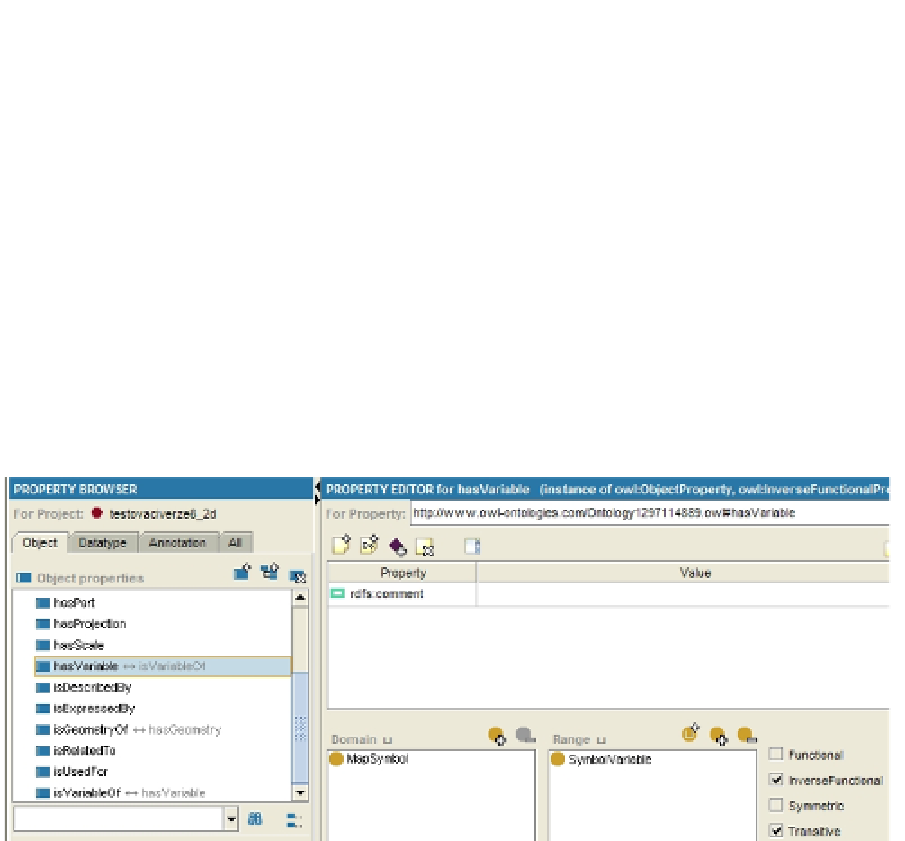
Fig. 9. List of object properties in Protégé (properties “hasVariable”)
Very carefully was designed the
hierarchy
of classes. The relation of two classes is expressed
by
subsumption
,
equivalence
or
disjunction
. The example of subsumption is upper class
AttributeData
and two sub class
QualitativeData
and
QuantitativeData
. The disjunction is also
defined for these two classes. When data have qualitative value they can not have
quantitative value. The terms isoline, isopleth and isochor are the example of equivalence
(synonyms) (Penaz, 2010).
The important part of ontology is also the definition of
properties
. The property
constructs relation between classes or individuals. The name of the property contains verb