Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
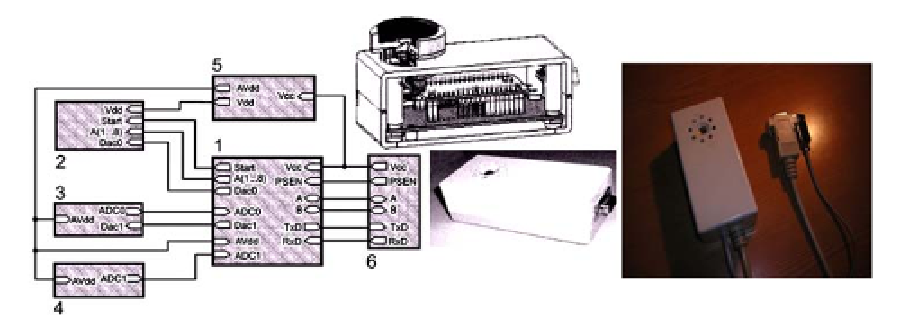
Fig. 1. Function circuit of the electron-optical module “ISSE” for a sensory system “CDOT”:
1 - microcontroller for the control and information processing; 2 - light-emitting
microdiodes control circuit; 3 - microphotodetector coupling; 4 - temperature monitoring
circuit; 5 - secondary voltage source; 6 - COM-port connector
characterizes a reflection coefficient from a reference surface used for the calibration of the
electronic optical module. The microprocessor-based device generating a soil sensory
information pattern processes the output signal of the microphotodetector [4]. Using “ISSE”
it is possible to analyze coefficients of absorption, refraction, light scattering, gradient
change, and polarization but also coefficients of variation (intensity, amplitude, and phase)
of the electromagnetic wave and a space-time field distribution. The obtained data of
spectroscopic analysis enable to produce an information pattern of soil, agricultural
products, foodstuff, and human biomatters. A gridded registrating unit periodic realizes the
real-time satellite navigation and the control of soil parameters. The specifically developed
software “ISSE” can be applied in an intelligent system “CDOT” (Control of Distribution of
Organics and Temperature) on a chip “electronic eye” which is of interest in precision
agriculture for the control of a soil humus-accumulative horizon at the depth of 20-30 to 180-
200 mm. A small intelligent sensory “mole” (“CDOT”) includes “ISSE” placed in the metal
sheathing with the stone and sunlight protection. The optical beam output to a controlled
soil surface is realized by the use of the sapphire transparent coating as the extra hard
material, so “CDOT” can be attached, e.g., to a mini-tractor or any other agricultural units.
“ISSE” explores the ground at the depth of 5-10 cm for the detection of organic substances,
moisture, temperature, colour, granulometric composition and for the analysis of the fertile
topsoil and using the GPS (Global Positioning System) navigation defines rapidly how
much exactly fertilizers have to be applied with the micromechatronic system in the specific
field place in process of optimal motion of the mini-tractor with an attached drawbar hitch
(Fig. 2) [1, 3, 4].
The given depth of penetration of the multisensory system “CDOT” for topsoil copying is
determined depending on structural features of the floor profile and on the location of the
humus-accumulative horizon. The hydralift system of the mini-tractor is intended for the
control of “CDOT” lifting and sinking actuators in soil. Positioning of the units is also based
on data from ultrasonic, microwave, electrostatic sensory modules at the same time. The
intelligent system “CDOT” fulfils data binding of a soil controlled information pattern to
ground control points from a GPS receiver and stores obtained data in its memory for