Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Data analysis stream
Image time-series
Kernel
Design matrix
Statistical parametric map (SPM)
or
Posterior probability map (PPM)
Realignment
Smoothing
General linear model
Normalization
Te m p l a t e
Parameter estimates
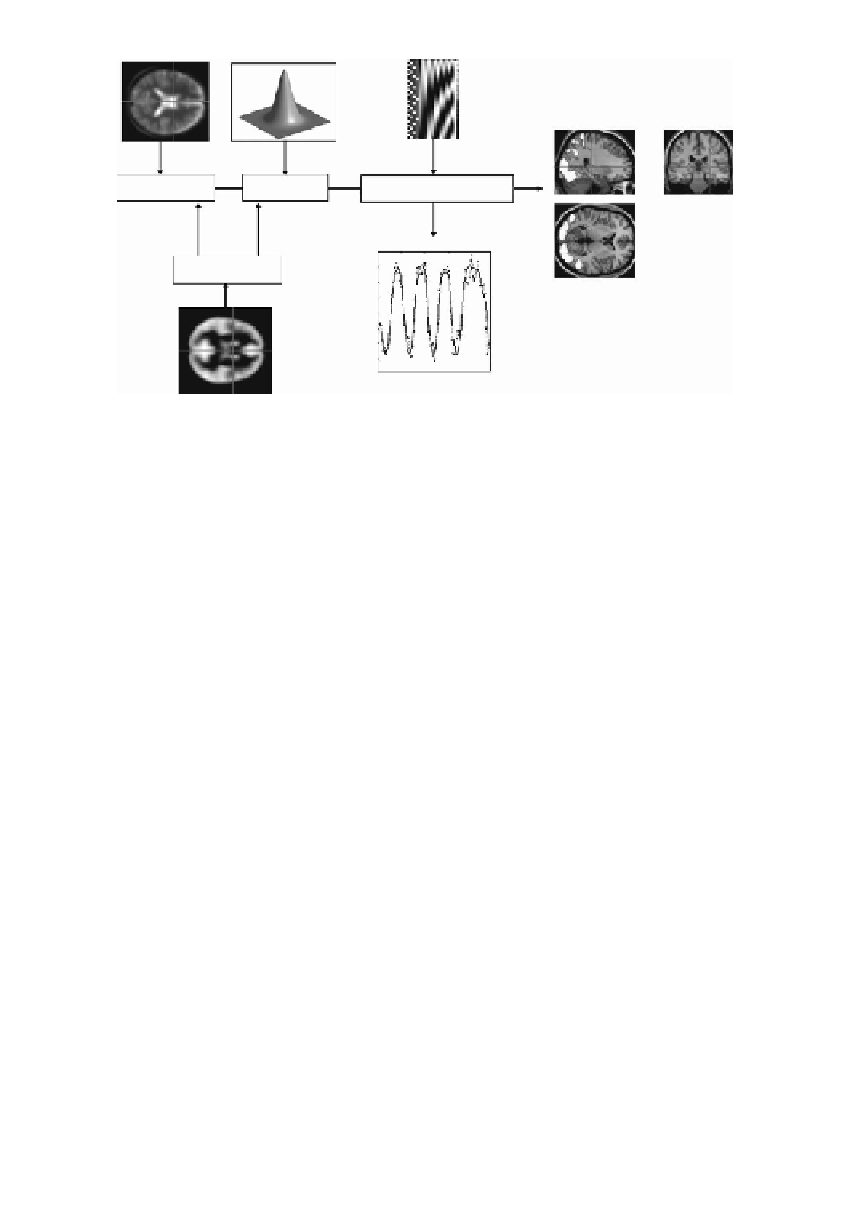
FIGURE 17.1
This schematic depicts the transformations that start with an imaging
data sequence and end with a statistical parametric map (SPM) or posterior probability
map (PPM). SPMs can be thought of as “x-rays” of the significance of an effect,
whereas PPMs reflect our confidence that the effect is larger than a certain specified
size. Voxel-based analyses require the data to be in the same anatomical space: This
is effected by realigning the data (and removing movement-related signal components
that persist after realignment). After realignment, the images are subject to nonlinear
warping so that they match a template that already conforms to a standard anatomical
space. After smoothing, the general linear model is employed to (1) estimate the
parameters of the model and (2) derive the appropriate univariate test statistic at every
voxel.
17.2
SPATIAL TRANSFORMATIONS
The analysis of neuroimaging data generally starts with a series of spatial trans-
formations. These transformations aim to reduce unwanted variance components
in the voxel time series that are induced by movement or shape differences among
a series of scans. Subsequent analyses assume that the data from a particular
voxel all derive from the same part of the brain. Violations of this assumption
will introduce artifactual changes in the voxel values that may obscure changes
or differences of interest. Even single-subject analyses proceed in a standard
anatomical space, simply to enable reporting of regionally specific effects in a
frame of reference that can be related to other studies.
The first step is to realign the data to “undo” the effects of subject movement
during the scanning session. After realignment, the data are then transformed
using linear or nonlinear warps into a standard anatomical space. Finally, the data
are usually smoothed spatially prior to analysis with a GLM.





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search