Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
−
0.2
0
20
40
60
80
−
80
−
60
−
40
−
20
x
(mm)
(a)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
−
0.2
−
80
−
60
−
40
−
20
0
20
40
60
80
x
(mm)
(b)
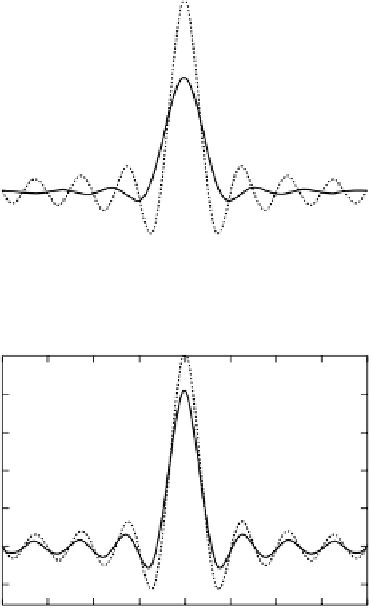
FIGURE 11.18
The influence of (a) a cosine filter and (b) a Hamming filter on the point-
spread function shape (solid) in comparison to the original PSF (dashed) (FOV
x
= 160 mm,
N
x
= 16, symmetrical sampling).
where N
exc
is the total number of excitations. Analogous to postacquisition filter-
ing, the value of A
lmn
is maximal in the center of the k-space, where A
lmn
equals
the number of averages N
acq
of the sequence.
It is obvious that apodization during the measurement can only be properly
performed when the total number of excitations N
exc
is sufficient to approximate
filter function w(l,m,n) by fractional weights A
lmn
. Because in the case of
1
H
CSI usually only a few averages are needed, an exclusive acquisition weighting
is used for nonhydrogen nuclei, which require more averages due to sensitivity
reasons. When the number of total excitations N
exc
is small, multiplication of
k-space data by a correction smoothing filter, to prevent ringing from sharp digital
transitions in weighting, should be performed (48).
Apodization can be generally accomplished by any combination of acquisi-
tion k-space weighting and the postacquisition filtering. This is the case in reality,






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search