Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
rf
G
z
G
y
G
x
Signal
0
10
20
Time (ms)
30
40
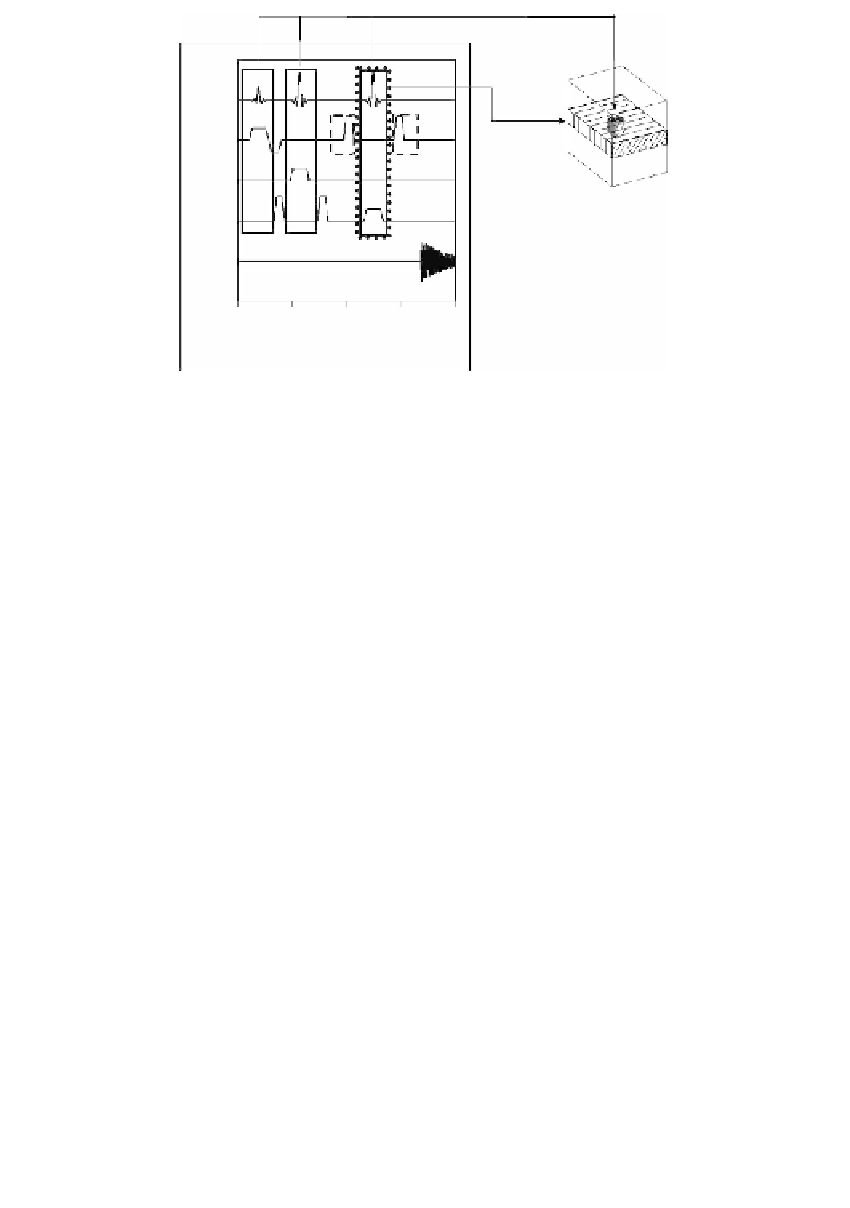
FIGURE 11.6
The different parts within the PRESS sequence. The combination of the
three RF pulses (denoted by bold lines) leads to the excitation of the selected voxel. The
unwanted signal contributions originating from the last pulse (denoted by dotted lines),
which excites the shown slice, can be strongly reduced by additional spoiler gradients
(denoted by dashed lines). The signal from the region of interest is not affected by the
spoiler gradients due to the effect of the refocusing 180
°
pulse.
Because there are several crusher gradients in the sequences and various
unwanted coherences are dephased differently, the order of the slice selection
gradients has a pronounced effect on the overall performance of the sequence
and, hence, on the achieved spectral quality (7).
Another problem in volume-selective spectroscopy is the chemical shift dis-
placement. The origin of this artifact is the same as the chemical shift artifact in
MR imaging: The resonance frequency of protons in different molecular sur-
roundings varies and, therefore, the exact localization of the selected slice depends
on the resonance frequency of the protons. The spatial difference between exci-
tation profiles for protons with a difference
∆ω
in the resonance frequency is
∆
x
=
∆
ω
/
γ
G
where
γ
is the gyromagnetic ratio and G the strength of the field gradient applied
simultaneously with the RF pulse (
Figure 11.7a
and Figure 11.7b). This effect occurs
with all three excitations of a PRESS or STEAM sequence and leads to a diagonal
shift of the voxel position that is dependent on the resonance frequency difference of
the protons (Figure 11.7c and Figure 11.7d). Because in H-MRS it is not the water
signal that is of interest but the signal of the metabolites, the resonance frequency of
the MR system is often adjusted to the resonance frequency of one of the major
metabolites (NAA in brain measurements). Nevertheless, it should be noted that the
exact localization of the selected region of interest is different for different metabolites





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search