Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
10.4.3
CSPAMM HARP
An improvement to the original HARP technique was proposed by Kuijer et al.
[31], who noted that the HARP angle is corrupted by a signal from other spectral
peaks, particularly the signal arising from T1 relaxation. The effect of T1 relax-
ation is to modify Equation 12 to
Mt
( , )
x
=
(
M
cos(
k
⋅
X
)
−
M
) exp(
−
t T M
/
1
)
+
(10.17)
z
0
e
0
0
This gives rise to a peak at the center of k-space, which grows with time, as
the harmonic peaks decrease with time. To avoid corruption of the HARP image
by this signal, the k-space filter is typically kept small (e.g., 32
×
32 pixels),
resulting in a low-resolution displacement map. By employing a 1
1 CSPAMM
tagging procedure, subtraction of the complementary signals cancels the central
peak and only two peaks remain, either of which can be used to construct the
HARP image. The size of the filter used to extract the peak can then be enlarged,
resulting in a higher resolution displacement map.
−
10.5
PHASE-CONTRAST VELOCITY
Although only magnitude images have been considered in the preceding section,
the phase of the MR image is also typically available, because the MR signal
acquisition is usually done in quadrature. This phase can be made sensitive to
motion using velocity-encoding gradients. In the classical pulsed gradient spin
echo experiment [32], two velocity-encoding gradients are used for this purpose
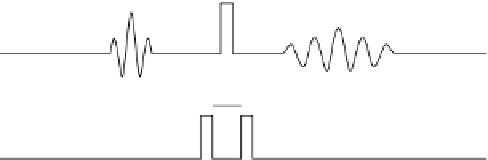
(Figure 10.9).
Spins that do not move during the time interval
∆
refocus with no phase offset.
g
.
u
For spins that coherently move an amount
u
during
∆
, the phase shift is
φ
=γδ
(assuming an ideal gradient profile). If the time interval
∆
is kept small, there is
little time for T2 decay, and the displacement over
∆
can be used as an estimate
of velocity.
The gradient echo version of this sequence is shown in
Figure 10.10
.
Here a bipolar gradient allows encoding of displacement over shorter time
intervals, at the cost of T2* decay. In practice, two scans must be acquired with
180
90
Signal
rf
∆
g
δ
FIGURE 10.9
Pulse gradient spin echo pulse sequence in which displacement between
the two gradients is encoded in the phase of the MR signal.










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search