Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
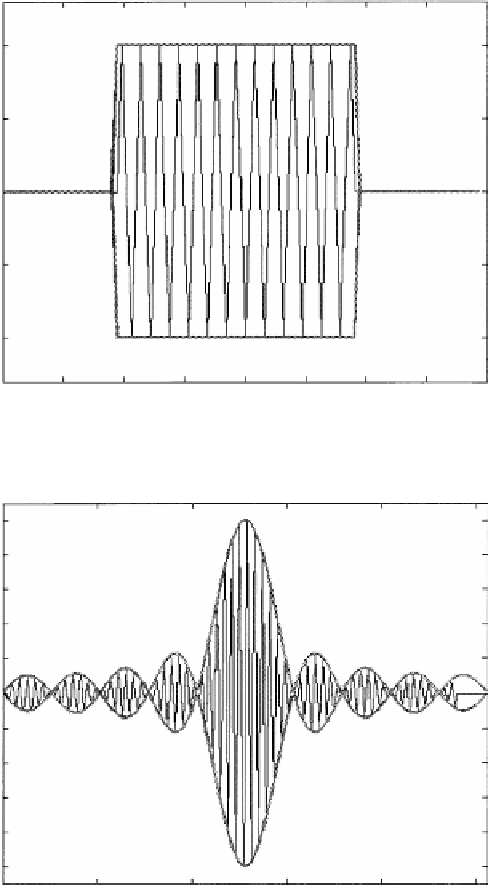
Rectangular RF pulse
t
(a)
Sinc RF pulse
t
(b)
FIGURE 1.5
Typical RF pulse shapes: (a) rectangular pulse, (b) sinc pulse.
) pulse, will place
M
along the negative
z
axis. This is often called
an
inversion pulse
. In general, for a constant
B
1
amplitude, an
π
(or 180
°
α
pulse causes
the magnetization vector
M
to precess through the flip angle:
α
=
γ
B
1
τ
(1.16)






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search