Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
5.8.5 Electro-reductive Polymerization
of Aromatic Monomers
Aromatic dihalides are representative
monomers for electroreductive polymerization.
Cathodic reduction of an aromatic dihalide
generates a radical anion, followed by
polymerization accompanying elimination of
halide (
Eq. 5.37
). Bond formation takes place at
the specific position of the monomer where the
halogen atom is substituted.
(5.37)
On electroreductive polymerization of
1,4-dibromopyridine, addition of a catalytic
amount of nickel(II) complex is effective and
the complex works as a mediator.
Electrogenerated nickel(0) promotes
dehalogenation of the dibromopyridine
followed by its polymerization [96].
Electro-oxidative polymerization of pyridine is
difficult because of its high oxidation potential,
but this reductive polymerization enables
polypyridines to be produced.
Poly(
p
-phenylene vinylene) is also synthesized
by electroreductive polymerization. As shown in
Eq. 5.38
, the electrochemical reduction of
α,α,α′,α′-tetrabromo-
p
-xylene generates a
quinodimethane
intermediate
and
its
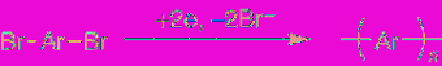
Search WWH ::

Custom Search