Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(5.18)
Recently, a sacrificial metal anode was used in
electrosynthesis. The resulting metal ions
derived from the anode, e.g. Mg, Zn, Al and, Cu,
often play important roles in electrochemical
reactions. These metal ions and cathodically
generated reactive species form highly reactive
intermediates new reagents or trap halide ions
generated by cathodic reduction of silyl
chlorides to polysilanes (see section 5.8.6) [62].
Moreover, such anodically dissolving metal ions
significantly affect regiochemistry,
stereochemistry and product selectivity by their
coordination and catalytic effects as well as
formation of a new reagents
in situ
[63]. For
instance, as shown in
Figure 5.15
, zinc ion
generated from the anode and trifluoromethyl
anion cathodically derived from CF
3
Br forms an
organometallic compound as an intermediate,
which undergoes a Reformatsky type reaction
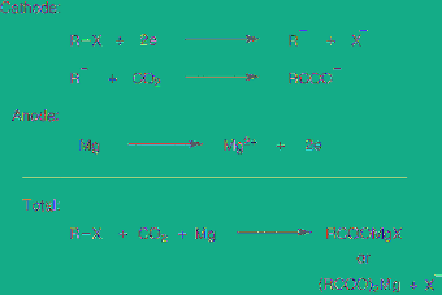
Search WWH ::

Custom Search