Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
are the most easily reduced, while chloride
compounds are the most difficult to reduce.
One-electron and two-electron reduction of
alkyl halides generate alkyl radicals and alkyl
anions, respectively.
(4.89)
Reduction of Ketone and Imine:
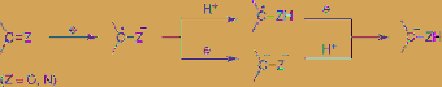
In the
case of cathodic reduction of ketone and imine
in aqueous solution, the generated reactive
species as well as the reaction mechanism are
changed by the pH of the solution. In an acidic
solution, the oxygen atom of the ketone and the
nitrogen atom of the imine are protonated,
therefore their reduction potentials shifts to the
positive side, and their one-electron reduction
generates neutral radicals. In contrast, in an
alkaline solution the protonation of ketone and
imine does not occur due to low proton
concentration. In this case, the radical anion is
generated first, and then the dianion is formed.
(4.90)
Reduction of Activated Olefin and
Conjugated Olefin:
Activated olefin is readily
reduced because the electron-withdrawing
group attached to the double bond decreases
the electron density of the double bond.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search