Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(4.17)
4.5.3 Electroauxiliaries Based on
Intermolecular Coordination Effects
This effect is quite important from an electron
transfer aspect. The electron transfer reaction
in solution is generally facilitated by the
stabilization of the resulting radical ion and
ionic intermediates by the coordination of
solvent molecules or counter ions in the
solution. For instance, the reduction potential
of the metal cation usually becomes more
negative in solvents with large donor numbers
because the positive nature of the metal cation
is decreased by solvation in such solvents.
It is well known that the reduction potentials of
ketones, imines, cyano and nitro compounds
shift in the positive direction by proton
addition. The polarography of the reduction of
nitro compounds has been intensively studied.
When the pH value of the solution is made
more acidic by one pH unit, the reduction
potential becomes more positive by about 58
mV. The positive shift of the reduction potential
is due to the protonation of unsaturated
functional groups resulting in a positively
charged form, as shown in
Figure 4.13
.
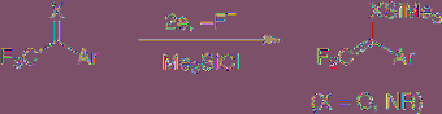
Search WWH ::

Custom Search