Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
4.3.2.4 Stereoselectivity
(a) Stereoselectivity Controlled by Selective
Adsorption of Reactive Intermediate to
Electrode
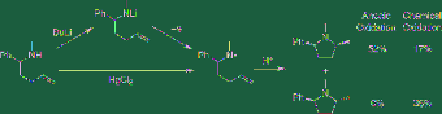
As shown in
Figure 4.6
, the lithium salt of an
unsaturated amine derivative adsorbs on the
anode due to coulombic interactions.
One-electron transfer then takes place to
generate the corresponding aminyl radical
intermediate, which undergoes subsequent
intramolecular cyclization in an adsorbed
manner or near the anode to result in
predominant formation of the
thermodynamically less stable
cis
-form product
[14]. Interestingly, in this reaction the
thermodynamically
favoured
trans
-form
product is not generated at all.
Figure 4.6
Stereoselective anodic cyclization
On the other hand, a similar reaction using a
chemical oxidant such as HgCl
2
provides
mainly the thermodynamically favourable
trans
product. Such high stereoselectivity in
electrochemical reactions is mainly attributable
to the adsorption effect. Thus, it can be stated
that the electrode contributes greatly to
Search WWH ::

Custom Search