Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
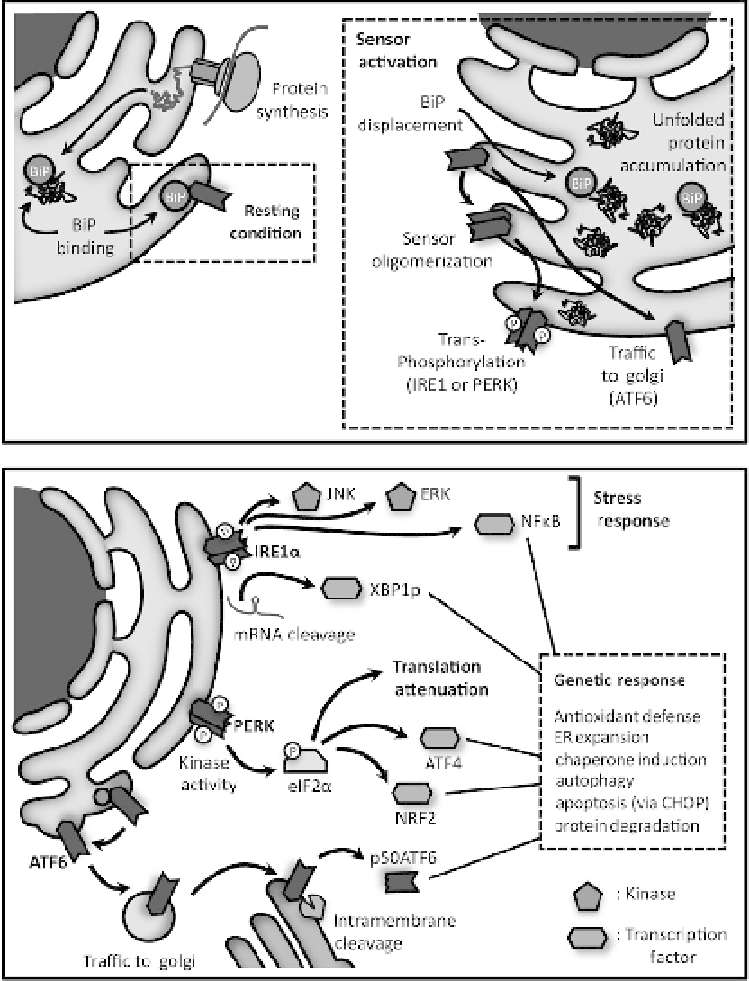
Figure 5.2
ER stress signaling
. Upper panel: In resting conditions, the stress sensors
IRE1 and PERK and ATF6 interact with Bip/GRP78. Accumulation of misfolded proteins
in the ER lumen separates the chaperone from each sensor. IRE1
α
and PERK activation
involves oligomerization and transphosphorylation of their cytosolic effector region.
ATF6 activation, on the other hand, requires its transport to the Golgi, where it is
sequentially cleaved by S1P and S2P. A recent model for IRE1
α
activation, involves an
initial dissociation of BiP/GRP78 that drives sensor oligomerization, while subsequent
binding to unfolded proteins leads to activation. Lower panel: The signaling engaged
by the three sensors activates several transcription factors (XBP1, ATF4, p50ATF6, NF-
κ
B,
CHOP) and protein kinases (JNK, AKT), leading to the establishment of a genetic pro-
gram termed unfolded protein response. This adaptive response involves chaperone
induction, activation of degradation pathways like the proteasome and autophagy, ER
expansion and increased antioxidant defense. Also, the PERK pathway inhibits general
mRNA translation, through eIF2
α
phosphorylation. If the cell does not reduce the mis-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search