Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
cells are cocultured with macrophages treated with either rapamycin or
TSC2 siRNA, respectively (
Chen et al., 2012b
).
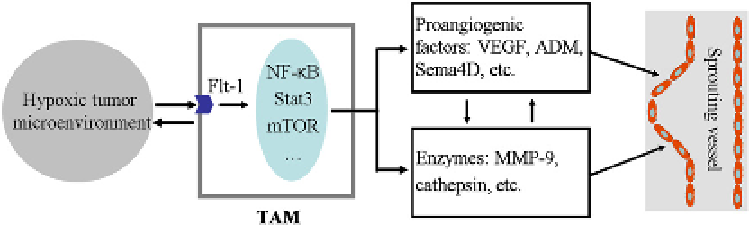
In summary, when TAMs are attracted to the hypoxic areas of tumor
site, they produce a large body of proangiogenic factors in addition to
angiogenesis-modulating enzymes, under the regulation of specific signal-
ing pathways (i.e. NF-κB and mTOR) and transcription factors (i.e. Stat3),
which together or partly contribute to tumor angiogenesis (
Fig. 1.2
). On
the other hand, TAMs may also promote tumor angiogenesis by affecting
other components, such as cancer cells, in the tumor microenvironment.
For example, the interaction of mouse breast cancer cells and TAMs leads to
the upregulation of Fra-1, a member of the FOS transcription factor family,
which in turn induces activation of the IL-6/JAK/Stat3 signaling path-
way in TAMs. This leads to increased release of the proangiogenic factors
MMP9,VEGF and TGF-β by cancer cells, thus promoting tumor angiogen-
esis (
Luo et al., 2010
).
5.2. Role of Macrophage Polarization
Although most studies reported that TAMs usually favor tumor angiogen-
esis, this effect is largely dependent on TAM phenotypes. Increasing evi-
dence demonstrate that TAMs normally exhibit the M2 (proangiogenic)
phenotype, which promotes endothelial cell proliferation and tumor angio-
genesis (
Lewis and Pollard, 2006
). However, in some cases, such as in the
Figure 1.2
Proangiogenic function of macrophages and its molecular nature in tumors
.
Following the attraction into hypoxic areas in tumors, signals from tumor microenviron-
ment induce macrophages activation by their cell surface receptors. During the process
of macrophage activation, specific signaling pathways (including NF-
κ
B and mTOR) and
transcription factors (such as Stat3) are activated, leading to the secretion of proangio-
genic factors (such as VEGF, PlGF, Sema4D, bFGF, IL-1, ADM and IL-8), and the production
of angiogenesis-modulated enzymes (such as cathepsin proteases, COX-2 and matrix
metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, and MMP-12). These proangiogenic fac-
tors and enzymes contribute to tumor angiogenesis. For color version of this figure, the
reader is referred to the online version of this topic.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search