Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
brain is believed to be one of the primary guidance cues that guide axons
of the hippocampal commissure to the other side of the brain (
Barallobre
et al., 2000
;
Serafini et al., 1996
;
Steup et al., 2000
).
Because the dorsal hippocampal commissure is also absent in CNS-
Act-
b
KO mice, we hypothesized that the axons of the corpus callosum lacked
their normal growth substrate and sought to determine if the hippocampal
neurons exhibited an impaired response to netrin-1. To accomplish this,
we took advantage of the previously described increase in hippocampal
neuron axonal branching following exposure to netrin-1 as a readout for
axonal responsiveness (
Popko et al., 2009
). Axonal branching is relatively
simple to measure and shares many common features with growth cone
turning including localized actin polymerization and Ca
2+
signals (
Dent
et al., 2003
,
2004
), although there are differences as well. Using this axonal
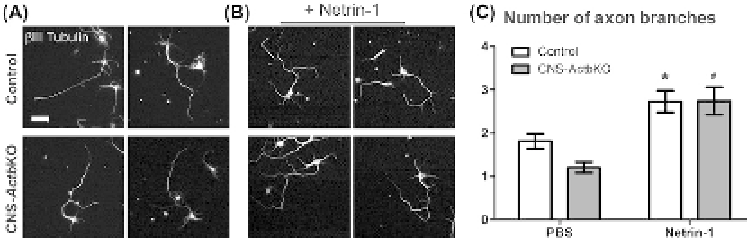
branching paradigm, we found that neurons devoid of β-actin protein by
immunofluorescence (
Cheever et al., 2012
) exhibited a similar increase in
axonal branching to netrin-1 as compared to controls (
Fig. 4.3
), suggesting
that downstream signaling from the netrin-1 receptor deleted in colorec-
tal cancer does not require local β-actin translation. Why β-actin-deficient
axons of the hippocampal commissure fail to cross the midline is still not
entirely clear, although we favor the hypothesis that disruptions in the local
hippocampal architecture (Section
5.1.2
) likely play a prominent role since
only axons extending through this region appear perturbed. If β-actin was
Figure 4.3
Netrin-1 induced axonal branching in control and β-actin KO hippocampal
neurons.
(A-B) Representative images of
β
III-tubulin-stained primary hippocampal neu-
rons cultured from control and CNS-
Actb
KO embryos. Neurons were treated with a bath
application of either PBS or 250 ng/ml netrin-1 for 3 days followed by fixation, stain-
ing and analysis. (C)
β
β-actin-deficient neurons showed a comparable increase in axonal
branching in response to netrin-1 as control neurons. * denotes significantly different
than control neurons treated with PBS. # indicates significantly different than
β
-actin KO
neurons treated with PBS.
n
> 100 neurons for each genotype from at least two inde-
pendent experiments. Scale bar 20 µm. Representative control images for comparison
from
Cheever et al. (2012).

Search WWH ::

Custom Search